
Pennsylvania
Keystone Exams
Pennsylvania Department of Education Bureau of Curriculum, Assessment and Instruction—August 2022
Biology
Item and Scoring Sampler
2022–2023

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
Introduction .................................................................1
About the Keystone Exams .....................................................1
Alignment ...............................................................2
Depth of Knowledge .......................................................2
Exam Format .............................................................2
Item and Scoring Sampler Format ................................................3
Biology Exam Directions .......................................................4
General Description of Scoring Guidelines for Biology ................................5
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Multiple-Choice Items .........................................................6
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................21
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................28
Biology Module 1—Summary Data ..............................................42
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Multiple-Choice Items ........................................................44
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................58
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................70
Biology Module 2—Summary Data ..............................................82

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
1
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
The Pennsylvania Department of Education (PDE) provides districts and schools with tools to assist
in delivering focused instructional programs aligned to the Pennsylvania Standards (PS). These tools
include the standards, Assessment Anchor documents, Keystone Exams Test Definition, Classroom
Diagnostic Tool, Standards Aligned System, and content-based item and scoring samplers. This
2022 Biology Item and Scoring Sampler is a useful tool for Pennsylvania educators in preparing
students for the Keystone Exams by providing samples of test item types and scored student
responses. The Item Sampler is not designed to be used as a pretest, a curriculum, or any other
benchmark for operational testing.
This Item and Scoring Sampler contains released operational multiple-choice and constructed-
response items that have appeared on previously administered Keystone Exams. These items will
not appear on any future Keystone Exams. Released items provide an idea of the types of items that
have appeared on operational exams and that will appear on future operational Keystone Exams.
Each item has been through a rigorous review process to ensure alignment with the Assessment
Anchors and Eligible Content. This sampler includes items that measure a variety of Assessment
Anchor and Eligible Content statements, but it does not include sample items for all Assessment
Anchor and Eligible Content statements.
The items in this sampler may be used
1
as samples of item types that students will encounter in
operational testing. Classroom teachers may find it beneficial to have students respond to the
constructed-response items in this sampler. Educators can then use the sampler as a guide to score
the responses either independently or together with colleagues.
This Item and Scoring Sampler is available in Braille format. For more information regarding Braille,
call (717)-901-2238.
ABOUT THE KEYSTONE EXAMS
The Keystone Exams are end-of-course assessments currently designed to assess proficiencies
in Algebra I, Biology, and Literature. For detailed information about how the Keystone Exams are
being integrated into the Pennsylvania graduation requirements, please contact the Pennsylvania
Department of Education or visit the PDE website at http://www.education.pa.gov.
1
The permission to copy and/or use these materials does not extend to commercial purposes.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
2
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
Alignment
The Biology Keystone Exam consists of questions grouped into two modules: Module 1—Cells and
Cell Processes and Module 2—Continuity and Unity of Life. Each module corresponds to specific
content, aligned to statements and specifications included in the course-specific Assessment
Anchor documents. The Biology content included in the Keystone Biology multiple-choice items will
align with the Assessment Anchors as defined by the Eligible Content statements. The process skills,
directives, and action statements will also specifically align with the Assessment Anchors as defined
by the Eligible Content statements.
The content included in Biology constructed-response items aligns with content included in the
Eligible Content statements. The process skills, directives, and action statements included in the
performance demands of the Biology constructed-response items align with specifications included
in the Assessment Anchor statements, the Anchor Descriptor statements, and/or the Eligible Content
statements. In other words, the verbs or action statements used in the constructed-response items
or stems can come from the Eligible Content, Anchor Descriptor, or Assessment Anchor statements.
Depth of Knowledge
Webb’s Depth of Knowledge (DOK) was created by Dr. Norman Webb of the Wisconsin Center for
Education Research. Webb’s definition of DOK is the cognitive expectation demanded by standards,
curricular activities, and assessment tasks. Webb’s DOK includes four levels, from the lowest (recall)
level to the highest (extended thinking) level.
Depth of Knowledge
Level 1 Recall
Level 2 Basic Application of Skill/Concept
Level 3 Strategic Thinking
Level 4 Extended Thinking
Each Keystone item has been through a rigorous review process and is assigned a DOK level. For
additional information about DOK, please visit the PDE website at http://static.pdesas.org/content/
documents/Keystone_Exams_Understanding_Depth_of_Knowledge_and_Cognitive_Complexity.pdf.
Exam Format
The Keystone Exams are delivered in a paper-and-pencil format as well as in a computer-based
online format. The multiple-choice items require students to select the best answer from four
possible answer options and record their answers in the spaces provided. The correct answer for
each multiple-choice item is worth onepoint. The constructed-response items require students
to develop and write (or construct) their responses. Constructed-response items in Biology are
scored using item-specific scoring guidelines based on a 0–3-point scale. Each multiple-choice item
is designed to take about one minute to one and a half minutes to complete. Each constructed-
response item is designed to take about eight minutes to complete. The estimated time to respond
to a test question is the same for both test formats. During an actual exam administration, students
are given additional time as necessary to complete the exam.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
3
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
ITEM AND SCORING SAMPLER FORMAT
This sampler includes the test directions and scoring guidelines that appear in the Keystone Exams.
Each sample multiple-choice item is followed by a table that includes the alignment, the answer
key, the DOK, the percentage
2
of students who chose each answer option, and a brief answer
option analysis or rationale. Each constructed-response item is followed by a table that includes
the item alignment, the DOK, and the mean student score. Additionally, each of the included item-
specific scoring guidelines is combined with sample student responses representing each score
point to form a practical item-specific scoring guide. The General Description of Scoring Guidelines
for Biology used to develop the item-specific scoring guidelines should be used if any additional
item-specific scoring guidelines are created for use within local instructional programs. The student
responses in this item and scoring sampler are actual student responses; however, the handwriting
has been changed to protect the students’ identities and to make the item and scoring sampler
accessible to as many people as possible.
Example Multiple-Choice Item Information Table
Item Information
Alignment Assigned AAEC
Answer Key Correct Answer
Depth of Knowledge Assigned DOK
p-value A Percentage of students who selected option A
p-value B Percentage of students who selected option B
p-value C Percentage of students who selected option C
p-value D Percentage of students who selected option D
Option Annotations Brief answer option analysis or rationale
Example Constructed-Response Item Information Table
Alignment
Assigned
AAEC
Depth of Knowledge
Assigned
DOK
Mean Score
Average
Score
2
All p-value percentages listed in the item information tables have been rounded.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
4
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
BIOLOGY EXAM DIRECTIONS
Directions:
Below are the exam directions available to students. These directions may be used to help students
navigate through the exam.
There are two types of questions in this module.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
These questions will ask you to select an answer from among four choices.
• Read each question, and choose the correct answer.
• Only one of the answers provided is correct.
• Record your answer in the Biology answer booklet.
Constructed-Response Questions:
These questions will require you to write your response.
• Be sure to read the directions carefully.
• You cannot receive the highest score for a constructed-response question without
following all directions.
• If the question asks you to do multiple tasks, be sure to complete all tasks.
• If the question asks you to explain, be sure to explain. If the question asks you to
analyze, describe, or compare, be sure to analyze, describe, or compare.
• All responses must be written in the appropriate location within the response box in the
Biology answer booklet. If you use scratch paper to write your draft, be sure to transfer
your final response to the Biology answer booklet.
In addition, a module may also include scenarios. A scenario contains text, graphics, charts, and/or
tables describing a biological concept, an experiment, or other scientific research. You can use the
information contained in a scenario to answer certain exam questions. Before responding to any
scenario questions, be sure to study the entire scenario and follow the directions for the scenario.
You may refer back to the scenario at any time when answering the scenario questions.
If you finish early, you may check your work in Module 1 [or Module 2] only.
• Do not look ahead at the questions in Module 2 [or back at the questions in Module 1] of
your exam materials.
• After you have checked your work, close your exam materials.
You may refer to this page at any time during this portion of the exam.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
5
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SCORING GUIDELINES FOR BIOLOGY
3 Points
• The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the scientific content, concepts,
and/or procedures required by the task(s).
• The response provides a clear, complete, and correct response as required by the task(s).
The response may contain a minor blemish or omission in work or explanation that does not
detract from demonstrating a thorough understanding.
2 Points
• The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the scientific content, concepts,
and/or procedures required by the task(s).
• The response is somewhat correct with partial understanding of the required scientific
content, concepts, and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may
contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1 Point
• The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the scientific content, concepts,
and/or procedures required by the task(s).
• The response is somewhat correct with minimal understanding of the required scientific
content, concepts, and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may
contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0 Points
• The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
scientific content, concepts, and/or procedures as required by the task(s).
• The response may show only information copied or rephrased from the question or
insufficient correct information to receive a score of 1.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
6
1
BiologyMODULE1
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEMS
1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms?
A. contain genetic material
B. contain membrane-bound organelles
C. use the same method of reproduction
D. use the same method of obtaining nutrition
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.1.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 56% (correct answer)
p-value B 23%
p-value C 12%
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations A. Key: Prokaryotes and eukaryotes both have genetic material, but it
is present in different forms among these groups.
B. Membrane-bound organelles are absent in prokaryotes but present
in eukaryotes.
C. Prokaryotes divide by binary fission; eukaryotes divide through the
process of mitosis.
D. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes both require energy, but the methods
used to obtain nutrients are not the same for all organisms.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
7
1
BiologyMODULE1
2. Which conclusion is best supported by the presence of ribosomes in prokaryotes and
eukaryotes?
A. Ribosomes have different functions in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
B. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes store energy to power life functions.
C. Ribosomes developed independently inside prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
D. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes make proteins to perform life functions.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 16%
p-value B 17%
p-value C 12%
p-value D 55% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. The function of a ribosome is to serve as the site of protein
synthesis in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
B. Energy in a cell is stored within the bonds of ATP, not ribosomes.
C. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, so their development
does not explain why they are found in both prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells.
D. Key: Ribosomes serve as the site of protein synthesis; eukaryotes
and prokaryotes are able to make proteins for cell growth and
repair.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
8
1
BiologyMODULE1
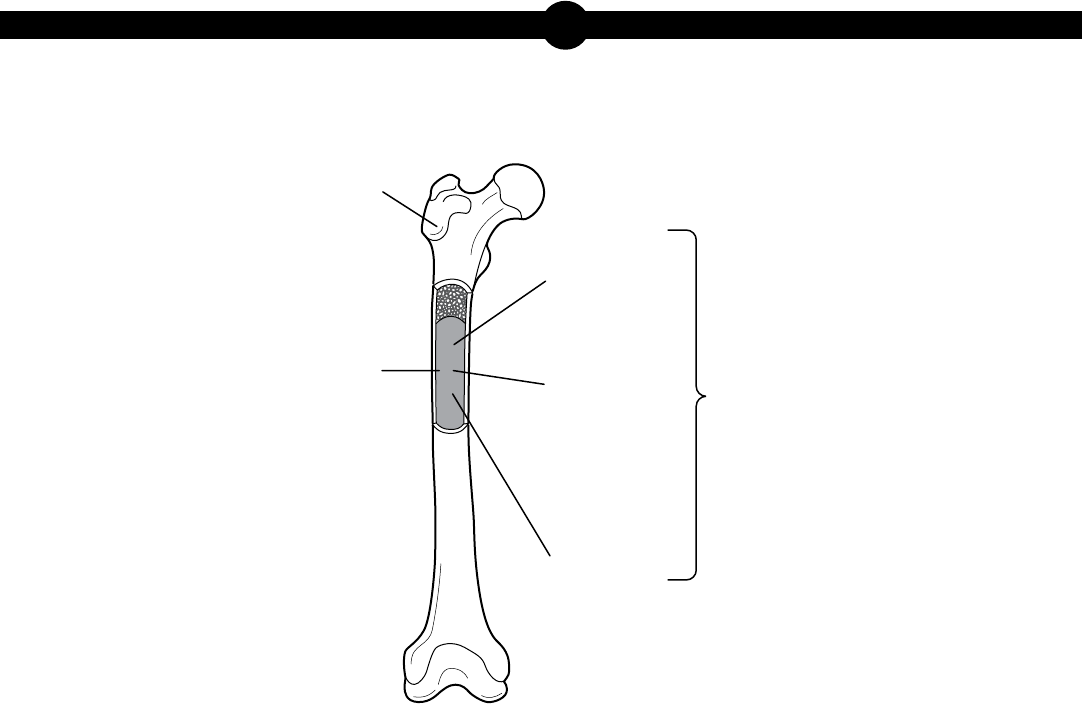
3. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
Some Components of a Bone
red blood
cells
bone
inside of
a bone
white blood
cells
platelets
marrow
The diagram shows a bone and some of its components. Which statement best describes a
relationship among some of these components?
A. Marrow is an organ in the skeletal system.
B. Marrow is a tissue that contains different types of cells.
C. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets perform the same function.
D. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets together form an organ system.
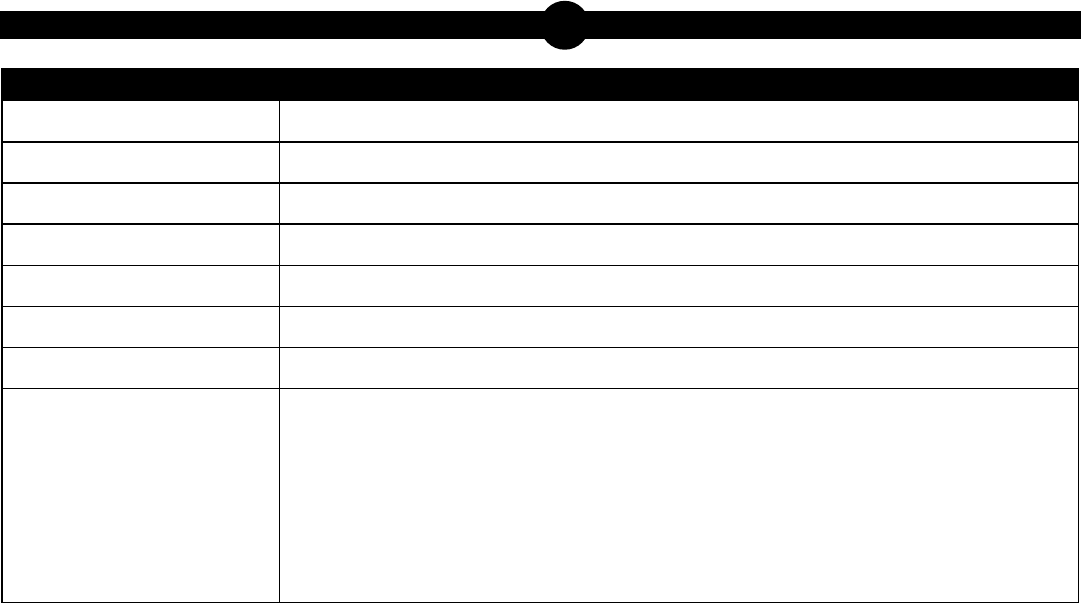
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
9
1
BiologyMODULE1
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.2.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 7%
p-value B 62% (correct answer)
p-value C 10%
p-value D 21%
Option Annotations A. Bone marrow is a tissue in bones, and bones are the organs in the
skeletal system.
B. Key: Bone marrow is a tissue in bone (an organ) and is made up of
specialized cells.
C. These different cell types have specialized forms and functions.
D. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are found in blood
and do not make up an organ system.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
10
1
BiologyMODULE1
4. Which statement best describes how amino acids become polymers?
A. Water is added as amino acids link to form proteins.
B. Water is released as amino acids break apart to form proteins.
C. Peptide bonds link amino acids together as proteins form.
D. Peptide bonds break between amino acids as proteins form.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.2.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 11%
p-value B 13%
p-value C 67% (correct answer)
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations A. To link amino acid monomers with peptide bonds, dehydration
synthesis releases water.
B. Hydrolysis can break peptide bonds, but this produces monomers,
not polymers.
C. Key: Amino acids become protein polymers through a condensation
(dehydration synthesis) reaction.
D. Amino acids are the monomers that link to form protein polymers.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
11
1
BiologyMODULE1
5. DNA replication in a eukaryotic cell occurs in the presence of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Which effect is most likely caused by a pH change in the cell nucleus?
A. The rate of DNA replication will decrease.
B. The energy required to initiate DNA replication will decrease.
C. DNA replication will occur in the absence of certain nucleic acids.
D. DNA replication will move to the cytoplasm and be completed by other enzymes.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.3.2
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 42% (correct answer)
p-value B 25%
p-value C 18%
p-value D 14%
Option Annotations A. Key: Enzymes function at a specific pH; any change above or
below this optimum pH will result in decreased activity of the
enzyme.
B. One function of an enzyme is to decrease activation energy, but
if the enzyme involved in the reaction is compromised, then the
energy to initiate a reaction will increase.
C. DNA is a nucleic acid and stores the genetic material.
D. DNA synthesis occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, not the
cytoplasm.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
12
1
BiologyMODULE1
6. Which statement best describes the role of ATP in a living system?
A. ATP senses and adjusts the pH in the cellular environment.
B. ATP identifies and repairs weak components of cells and tissues.
C. ATP measures and provides heat to increase reaction rates in cells.
D. ATP captures and transfers energy released by the breakdown of glucose.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 6%
p-value B 7%
p-value C 9%
p-value D 79% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. As a molecule, ATP is an energy carrier, and it does not have
sensory capabilities.
B. As a molecule, ATP is an energy carrier, and it provides the energy
for repairs to be performed.
C. ATP does not monitor conditions in the cellular environment.
D. Key: Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of the ATP molecule,
particularly the bonds between the phosphate groups.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
13
1
BiologyMODULE1
7. An organism carries out both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Which statement
describes a difference between these two processes?
A. Only cellular respiration creates chemical energy.
B. The processes occur in different types of animal cells.
C. Only photosynthesis changes light energy into chemical energy.
D. The processes occur at different times during the animal’s life cycle.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 10%
p-value B 7%
p-value C 76% (correct answer)
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations A. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration transform chemical energy.
B. Photosynthesis occurs in plant cells, not animal cells.
C. Key: Photosynthesis uses radiant energy from the Sun and converts
it into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
D. Photosynthesis occurs in plant cells, not animal cells.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
14
1
BiologyMODULE1
8. Which statement best describes both mitochondria and chloroplasts?
A. They both contain their own RNA and are involved in transcription.
B. They both contain their own DNA and are involved in energy conversions.
C. They both contain their own DNA and are involved in controlling the activities of a cell.
D. They both contain their own RNA and are involved in storage of nuclear genetic material.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.1.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 12%
p-value B 59% (correct answer)
p-value C 18%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A. They both contain RNA, but chloroplasts are involved in
photosynthesis and mitochondria produce cell energy in cellular
respiration.
B. Key: Mitochondria and chloroplasts both contain DNA and both
form ATP.
C. The nucleus controls the activities of a cell.
D. The nucleus of the cell stores the genetic material.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
15
1
BiologyMODULE1
9. A molecule is produced within a ribosome in a cell. What most likely happens to the newly
formed molecule once it is inside the Golgi apparatus of the cell?
A. It will be used to form new genetic material.
B. It will be stored for the cell’s future energy needs.
C. It will be modified before it is packaged for transport.
D. It will be broken down so its components can be reused.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.1.3
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 12%
p-value B 17%
p-value C 60% (correct answer)
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A. The Golgi apparatus does not replicate DNA for new genetic
material.
B. The Golgi apparatus does not have the ability to store cell materials
or energy molecules.
C. Key: The Golgi apparatus functions to process proteins and sort
them for transport.
D. The Golgi apparatus does not have the ability to break down
molecules; this is the role of lysosomes.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
16
1
BiologyMODULE1
10. In the human body, the steroid aldosterone is released by the adrenal glands to help regulate
sodium and potassium levels. This regulation helps control blood pressure and the balance of
fluids in blood. Which statement best describes this process of regulation within the body?
A. It is a feedback system that maintains homeostasis.
B. It is a response that is only a result of medical intervention.
C. It is a response by the body that is used only in extreme situations.
D. It is a feedback system that moves the body further from equilibrium.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 72% (correct answer)
p-value B 7%
p-value C 13%
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations A. Key: The hormone aldosterone helps regulate blood volume as part
of the negative feedback loop for water balance (homeostasis) in
the human body.
B. This regulation is a natural response by the body involving
interaction between the endocrine, circulatory, and excretory
systems.
C. Human body systems are constantly monitoring and responding to
changing environmental conditions, which means that this response
is part of the normal homeostatic process.
D. Positive feedback loops are less common in types of homeostasis
because they reinforce changes that push a variable further from
the steady state.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
17
1
BiologyMODULE1
11. Which statement best explains why most biological macromolecules contain carbon?
A. The long chains formed by carbon can be combusted with oxygen as a source of energy.
B. Carbon exists across the universe and is produced in the interior of stars during their life
cycles.
C. Carbon can share electrons with up to four different atoms and form three types of bonding
patterns.
D. The chemical and physical characteristics of carbon-containing molecules change as they
move through the carbon cycle.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.2.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 12%
p-value B 5%
p-value C 71% (correct answer)
p-value D 12%
Option Annotations A. Hydrocarbon chains are just one of many forms carbon can take,
and hydrogen is one of many atoms with which carbon can bond.
B. Carbon’s continual formation as stars evolve makes it universally
available to be incorporated into different molecules as a function
of its chemical characteristics.
C. Key: This ability to bond with many different atoms in different
forms and structures gives carbon the unique role of being present
in many molecules.
D. This characteristic allows carbon to be present in various forms on
Earth.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
18
1
BiologyMODULE1
Directions: Use the information presented on page 18 to answer questions 12 and13.
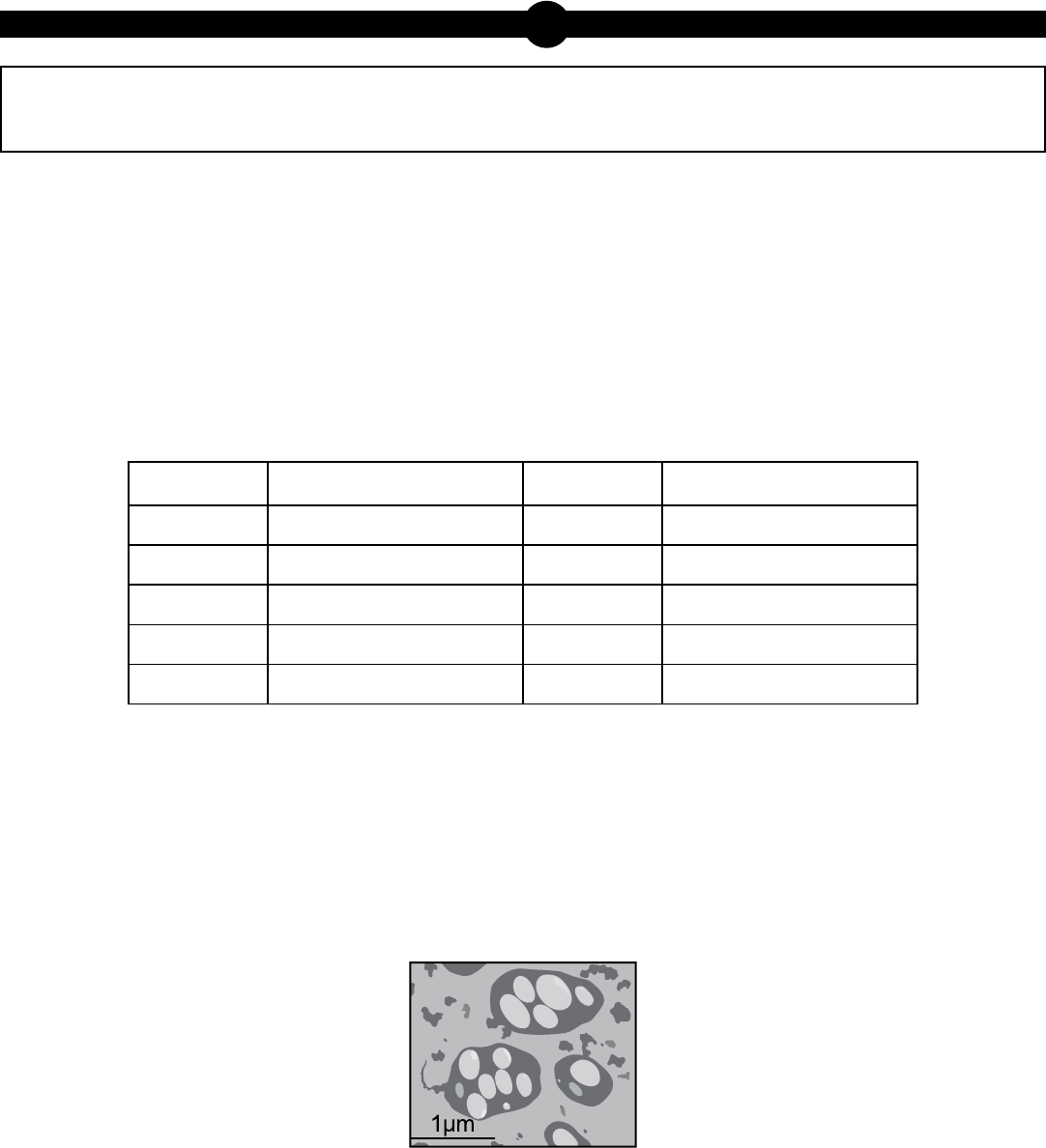
Arsenic-Loving Bacteria or Not
For many years, scientists thought that carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), sulfur (S),
and phosphorus (P) were necessary building blocks for all living things. These elements are required
to make many biological molecules. Recently, a scientist working for the National Aeronautics and
Space Administration (NASA) claimed to have discovered a bacterium that could use arsenate
(AsO
4
3-
) instead of phosphate (PO
4
3-
) as a building block for biological molecules. This bacterium,
GFAJ-1, lives in Mono Lake, a briny body of water located in central California.
Chemical Composition of Mono Lake
Element Concentration (g/L) Element Concentration (g/L)
Sodium 39.3 Phosphate 0.088
Chloride 23.0 Fluoride 0.065
Sulfate 13.1 Magnesium 0.044
Potassium 1.8 Silica 0.028
Boron 0.474 Arsenic 0.017
The NASA scientist collected mud from Mono Lake and added it to a container of salt medium.
This medium did not have PO
4
3-
but did have a high concentration of AsO
4
3-
. After diluting the mud
sample several times and adding more AsO
4
3-
, the scientist thought PO
4
3-
levels were too low for
any microbe to use. However, the scientist discovered one type of microbe, the bacterium GFAJ-1,
in the mud mixture that seemed to thrive when other microbes struggled to survive.
GFAJ-1
Further tests on GFAJ-1 seemed to confirm that the AsO
4
3-
had taken the place of PO
4
3-
in some
biological molecules, such as DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Other scientists were
unable to reproduce the NASA scientist’s results. They thought the samples used by the NASA
scientist likely contained PO
4
3-
contaminants that could still support GFAJ-1 growth. Finally, the
scientists determined the bacterium used a special protein to discriminate between PO
4
3-
and
AsO
4
3-
. This protein allowed the bacterium to reject the arsenate and accept the phosphate even
when the arsenate molecules outnumbered the phosphate molecules 4,500 to 1. Thus GFAJ-1
turned out to be a bacterium that was highly resistant to AsO
4
3-
and not an arsenic-loving bacterium.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
19
1
BiologyMODULE1
12. Which statement best explains how a property of water influences the chemical composition of
Mono Lake?
A. The nonpolar nature of water molecules allows water to neutralize ions.
B. The nonpolar nature of water molecules allows water to engulf the salts.
C. The polar nature of water molecules allows water to repel different salts.
D. The polar nature of water molecules allows water to form bonds with ions.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 16%
p-value B 15%
p-value C 18%
p-value D 51% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. Water molecules are polar and do not dissolve ions by undergoing
an acid-base reaction with them.
B. Water molecules are polar and tend to form hydrogen bonds with
each other to form cages around small, nonpolar molecules, not
salts.
C. Water molecules are polar, but they attract ions in salts, forming
covalent bonds with metal ions and hydrogen bonds with negative
ions.
D. Key: Water is polar and dissolves the compounds in the water.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
20
1
BiologyMODULE1
13. Based on the final conclusion scientists reached about GFAJ-1, what would happen to energy
production by the bacterium when given an arsenate-rich, phosphate-free medium?
A. Neither ADP nor ATP would be produced because the bacterium can only use PO
4
3-
, and
this would cause energy production to stop.
B. ADP and P
i
would continue to be converted into ATP using AsO
4
3-
instead of PO
4
3-
, and
this conversion would maintain energy production.
C. Neither ADP nor ATP would be produced because the bacterium has no mitochondria to
produce PO
4
3-
, and this would cause energy production to stop.
D. ADP and P
i
would continue to be converted into ATP using PO
4
3-
produced by the
mitochondria, and this conversion would maintain energy production.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.2
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 41% (correct answer)
p-value B 27%
p-value C 15%
p-value D 17%
Option Annotations A. Key: In the absence of phosphate, the bacterium would be unable
to produce energy.
B. The absence of phosphate and the toxicity of the arsenate would
prevent any synthesis of ADP, P
i
, or ATP.
C. GFAJ-1 has no mitochondria and absorbs PO
4
3-
from the
environment.
D. Bacteria do not have mitochondria, and mitochondria do not
produce PO
4
3-
.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
21
1
BiologyMODULE1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
14. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Observed Cell Features
Cell 1 Cell 2
• nucleoid
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• mitochondria
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
Using a microscope, a scientist observed two cells and recorded several features observed for
each cell.
Part A: The scientist recorded a limited number of observations for each cell.
Based on the information, classify each cell as either a prokaryote or a
eukaryote.
Cell 1:
Cell 2:
Part B: Identify another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is
not on the chart and describe the function of this cell structure.
Cell Structure:
Function:
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
22
1
BiologyMODULE1
SCORING GUIDE
#14 Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.2.1 Depth of Knowledge 3 Mean Score 1.41
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of comparing and contrasting
cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by
• classifying each of two cells as prokaryote or eukaryote, based on a chart of
observations for each cell,
AND
• identifying another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is not
on the chart,
AND
• describing the function of this cell structure.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting
cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by fulfilling
two of the bullets under the 3-point response. The response may contain some work
that is incomplete or unclear.
1
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of comparing and contrasting
cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by fulfilling
one of the bullets listed under the 3-point response. The response may contain some
work that is incomplete or unclear.
0
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
concept being tested.
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
23
1
BiologyMODULE1
Responses That Will Receive Credit
Part A (1 point):
• Cell 1 is a prokaryote and Cell 2 is a eukaryote
Part B (2 points total; 1 point for identifying the structure, 1 point for its function):
• Structure: DNA
OR
• Structure: ribosomes
OR
• Structure: cell wall
OR
• Structure: flagellum
• Function of DNA: carries the genetic information for the cell
OR
• Function of DNA: carries the instructions for the cell
OR
• Function of DNA: carries the genes that the cell needs
• Function of ribosomes: build proteins
OR
• Function of ribosomes: perform translation
• Function of cell wall: provides cell structure
OR
• Function of cell wall: protects the cell
OR
• Function of cell wall: prevents the cell from bursting
• Function of flagellum: helps the cell move; cell motility
Background Information:
• Not all eukaryotic cells have a cell wall or flagellum, but many do.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
24
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
14. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Observed Cell Features
Cell 1 Cell 2
• nucleoid
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• mitochondria
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
Using a microscope, a scientist observed two cells and recorded several features observed for
each cell.
Part A: The scientist recorded a limited number of observations for each cell.
Based on the information, classify each cell as either a prokaryote or a
eukaryote.
Cell 1:
Cell 2:
Part B: Identify another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is
not on the chart and describe the function of this cell structure.
Cell Structure:
Function:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
prokaryote
eukaryote
Flagella
The function is to help move the cell
around.
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of comparing and contrasting cellular structures and their
functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In Part A, the response correctly classifies each of the two cells as
prokaryote or eukaryote (Cell 1: prokaryote; Cell 2: eukaryote). In Part B, the response correctly identifies another cell
structure that would be observed in both cells but is not on the chart (Cell Structure: Flagella) and correctly describes
the function of this cell structure (Function: help move the cell around). The response is clear, complete, and correct.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
25
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
14. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Observed Cell Features
Cell 1 Cell 2
• nucleoid
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• mitochondria
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
Using a microscope, a scientist observed two cells and recorded several features observed for
each cell.
Part A: The scientist recorded a limited number of observations for each cell.
Based on the information, classify each cell as either a prokaryote or a
eukaryote.
Cell 1:
Cell 2:
Part B: Identify another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is
not on the chart and describe the function of this cell structure.
Cell Structure:
Function:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Prokaryote
Eukaryote
The cell membrane
It controls what enters and leaves a
cell.
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting cellular structures and their
functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In Part A, the response correctly classifies each of the two cells as
prokaryote or eukaryote (Cell 1: Prokaryote; Cell 2: Eukaryote). In Part B, the response incorrectly identifies another
cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is not on the chart (Cell Structure: cell membrane); cell (plasma)
membrane is included on the chart, so it does not receive credit. However, the response does correctly describe the
function of this cell structure (Function: controls what enters and leaves a cell).
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
26
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
14. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Observed Cell Features
Cell 1 Cell 2
• nucleoid
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• mitochondria
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
Using a microscope, a scientist observed two cells and recorded several features observed for
each cell.
Part A: The scientist recorded a limited number of observations for each cell.
Based on the information, classify each cell as either a prokaryote or a
eukaryote.
Cell 1:
Cell 2:
Part B: Identify another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is
not on the chart and describe the function of this cell structure.
Cell Structure:
Function:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
eukaryote
prokaryote
Rhobosome
Rhobosomes store water and energy in
thecell.
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of comparing and contrasting cellular structures and their
functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In Part A, the response incorrectly classifies both cells as prokaryote
or eukaryote (Cell 1: eukaryote; Cell 2: prokaryote) and does not receive any credit. In Part B, the response
correctly identifies another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is not on the chart (Cell Structure:
Rhobosome). However, the response incorrectly describes the function of ribosomes (store water and energy in the
cell), and the function description does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
27
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
14. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Observed Cell Features
Cell 1 Cell 2
• nucleoid
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• mitochondria
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
Using a microscope, a scientist observed two cells and recorded several features observed for
each cell.
Part A: The scientist recorded a limited number of observations for each cell.
Based on the information, classify each cell as either a prokaryote or a
eukaryote.
Cell 1:
Cell 2:
Part B: Identify another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is
not on the chart and describe the function of this cell structure.
Cell Structure:
Function:
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
eukaryote
prokaryote
Exocytosis
used to move materials out of the cell.
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of comparing and contrasting cellular
structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In Part A, the response incorrectly classifies both
cells as prokaryote or eukaryote (Cell 1: eukaryote; Cell 2: prokaryote) and does not receive any credit. In Part B, the
response incorrectly identifies another cell structure that would be observed in both cells but is not on the chart (Cell
Structure: Exocytosis). Exocytosis is not a cellular structure; the accompanying description of the function (used to
move materials out of the cell) does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
28
1
BiologyMODULE1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
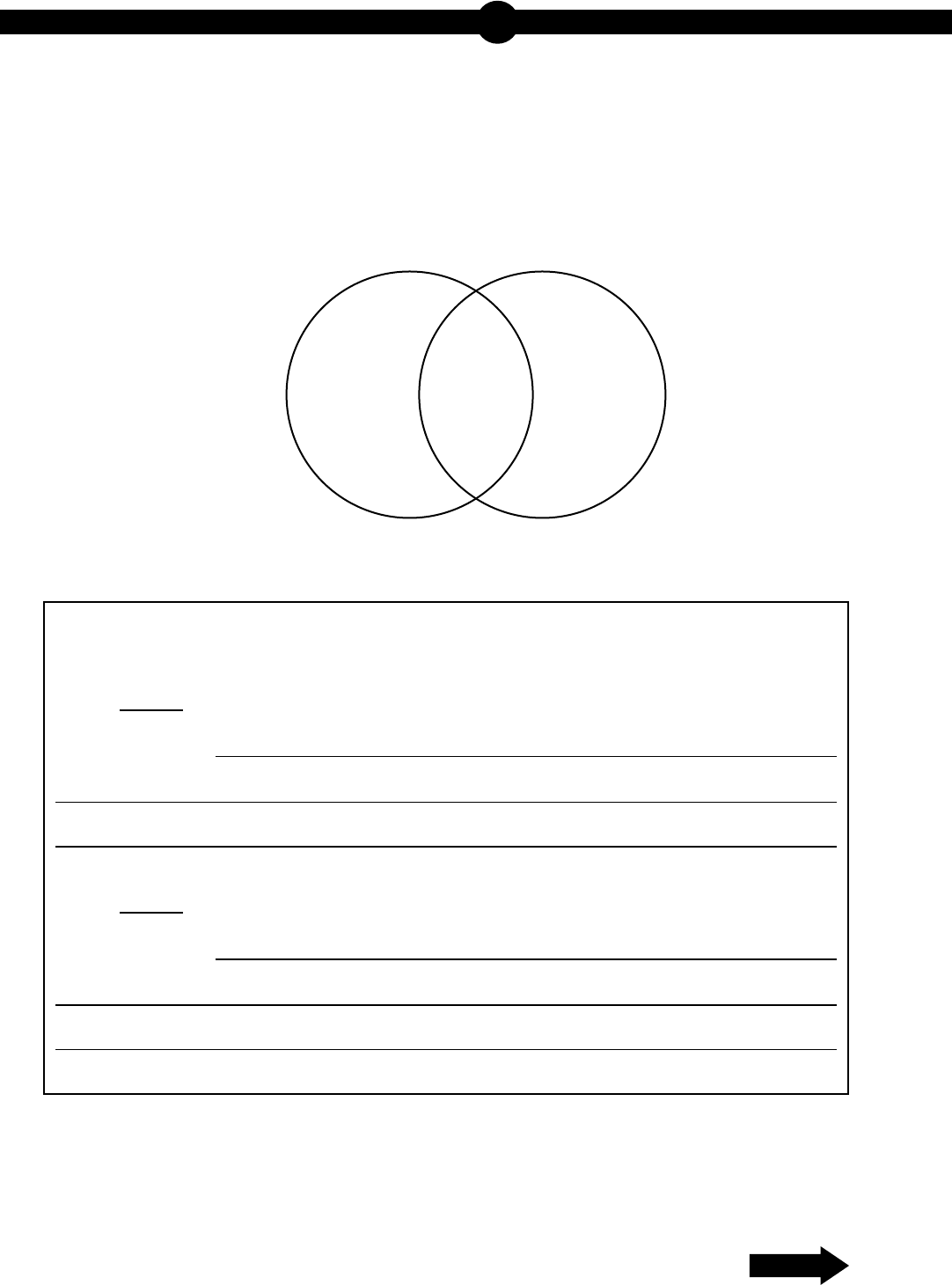
15. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
photosynthesis cellular respiration
area X area Zarea Y
Two Cellular Processes
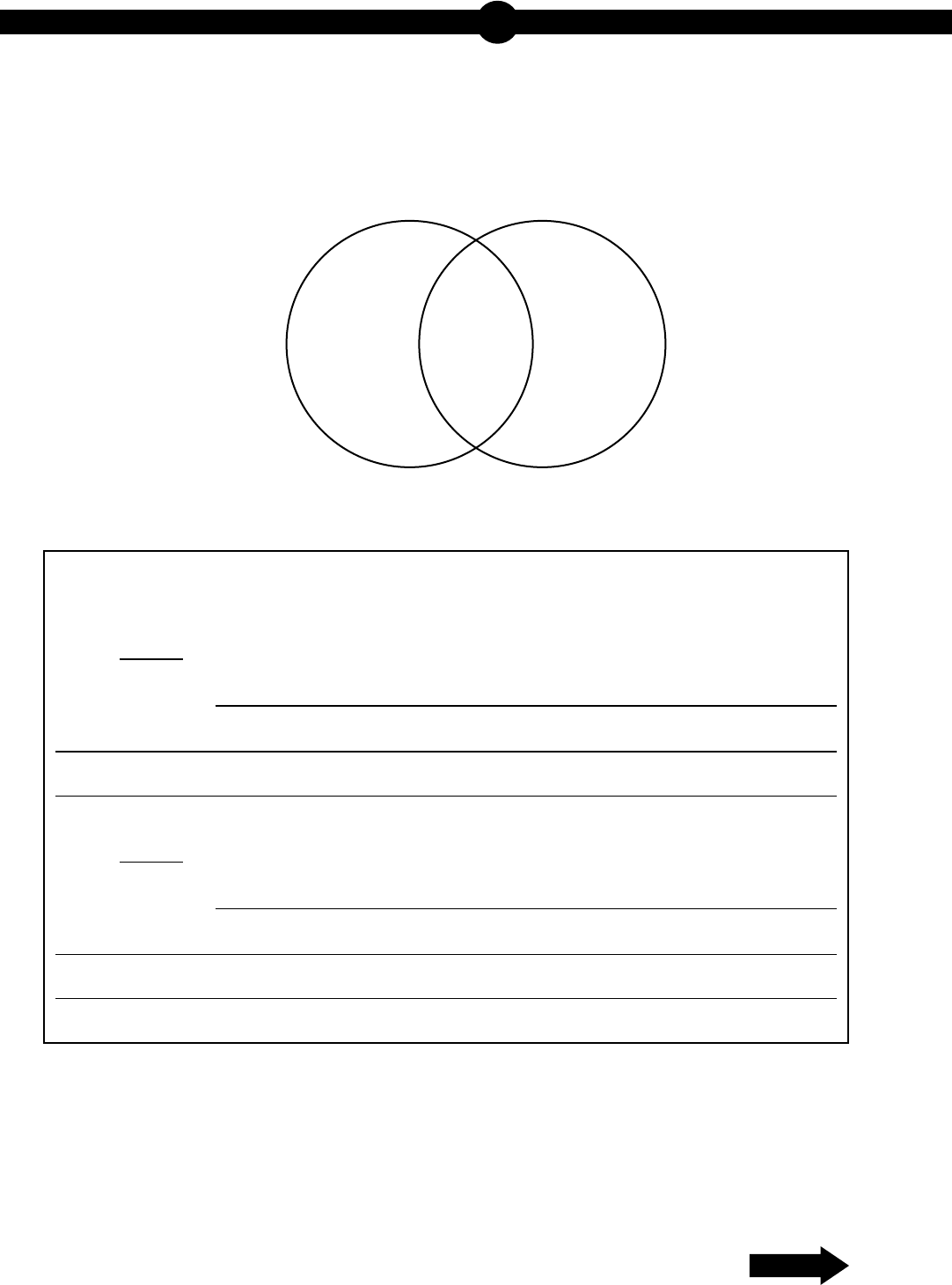
A student draws a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two cellular processes.
Part A: Select two areas from the Venn diagram and describe a characteristic that
could be placed into each of the areas.
Area:
Characteristic:
Area:
Characteristic:
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
29
1
BiologyMODULE1
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
30
1
BiologyMODULE1
SCORING GUIDE
#15 Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.1 Depth of Knowledge 3 Mean Score 1.39
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of comparing and contrasting
the basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration by
• describing a characteristic of one of three areas on a Venn diagram that shows
overlap between the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration,
AND
• describing a characteristic of a second of three areas on a Venn diagram
that shows overlap between the processes of photosynthesis and cellular
respiration,
AND
• explaining why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting
the basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration by
fulfilling two of the bullets under the 3-point response. The response may contain
some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of comparing and contrasting
the basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration
by fulfilling one of the bullets listed under the 3-point response. The response may
contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
concept being tested.
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
31
1
BiologyMODULE1
Responses That Will Receive Credit
Part A (2 points total; 1 point for each area with a characteristic):
Area X Characteristics:
• occurs only in plants, algae, and some bacteria
• happens in chloroplasts/chlorophyll
• uses sunlight energy
• generates oxygen
• makes sugars and other organic molecules/chemical energy
• includes the light-dependent reactions and/or the Calvin cycle
• fixes carbon
• uses carbon dioxide
• has two stages
Area Y Characteristics:
• both use an electron transport chain
• both use a cycle of enzymes
• both generate and use a proton-motive force (proton gradient)
• both make ATP
• both occur inside an organelle/a cell
• both use an organelle that probably originated as an endosymbiont
• both have multiple stages
• both use ATP synthase
• both use each other’s products as input
Area Z Characteristics:
• breaks down sugars or other organic molecules
• generates water
• has one stage that occurs in the cytosol
• occurs in the mitochondria
• includes glycolysis and/or the citric acid cycle
• requires oxygen
• has three/four stages
• generates carbon dioxide

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
32
1
BiologyMODULE1
Part B (1 point):
• Plants need to perform photosynthesis to make organic molecules as raw material for
growth, and they need to perform cellular respiration to make ATP to power the energy-
requiring processes in the cell.
OR
• Plants need to perform photosynthesis so they have molecules for growth and sugars that
can be broken down by cellular respiration to provide the energy for cellular work.
OR
• Cellular respiration makes ATP to power cell work; photosynthesis is how the organism
uses sunlight energy to make the organic molecules it needs.
OR
• Since plants don’t eat, they get their organic molecules from photosynthesis; they get the
energy for cellular work from cellular respiration.
Background Information:
• Photosynthesis includes two stages. The first is called the light reactions or the light-
dependent reactions. It uses sunlight energy to make ATP and NADPH, which requires an
electron transport chain to make a proton gradient. Then the proton gradient powers an
ATP synthase. This first stage uses water and generates oxygen. The second stage is called
the Calvin cycle or the light-independent reactions. It uses the energy stored in ATP and
NADPH to fix carbon, or add inorganic carbon dioxide to an organic molecule, eventually
making PGAL (aka G3P). Two PGAL molecules make one glucose.
• In cellular respiration, the citric acid cycle is also called the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle.
• In cellular respiration, there are four stages: glycolysis, an unnamed stage that is often
called the junction stage, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative
phosphorylation includes an electron transport chain (to generate a proton gradient) and
chemiosmosis (using the proton gradient to make ATP via ATP synthase).
• Photosynthesis makes ATP, but that ATP must stay in the chloroplast and be used to drive
the Calvin cycle; it is not available to do cellular work.
• A proton is also a hydrogen ion, or H
+
.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
33
1
BiologyMODULE1
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
34
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
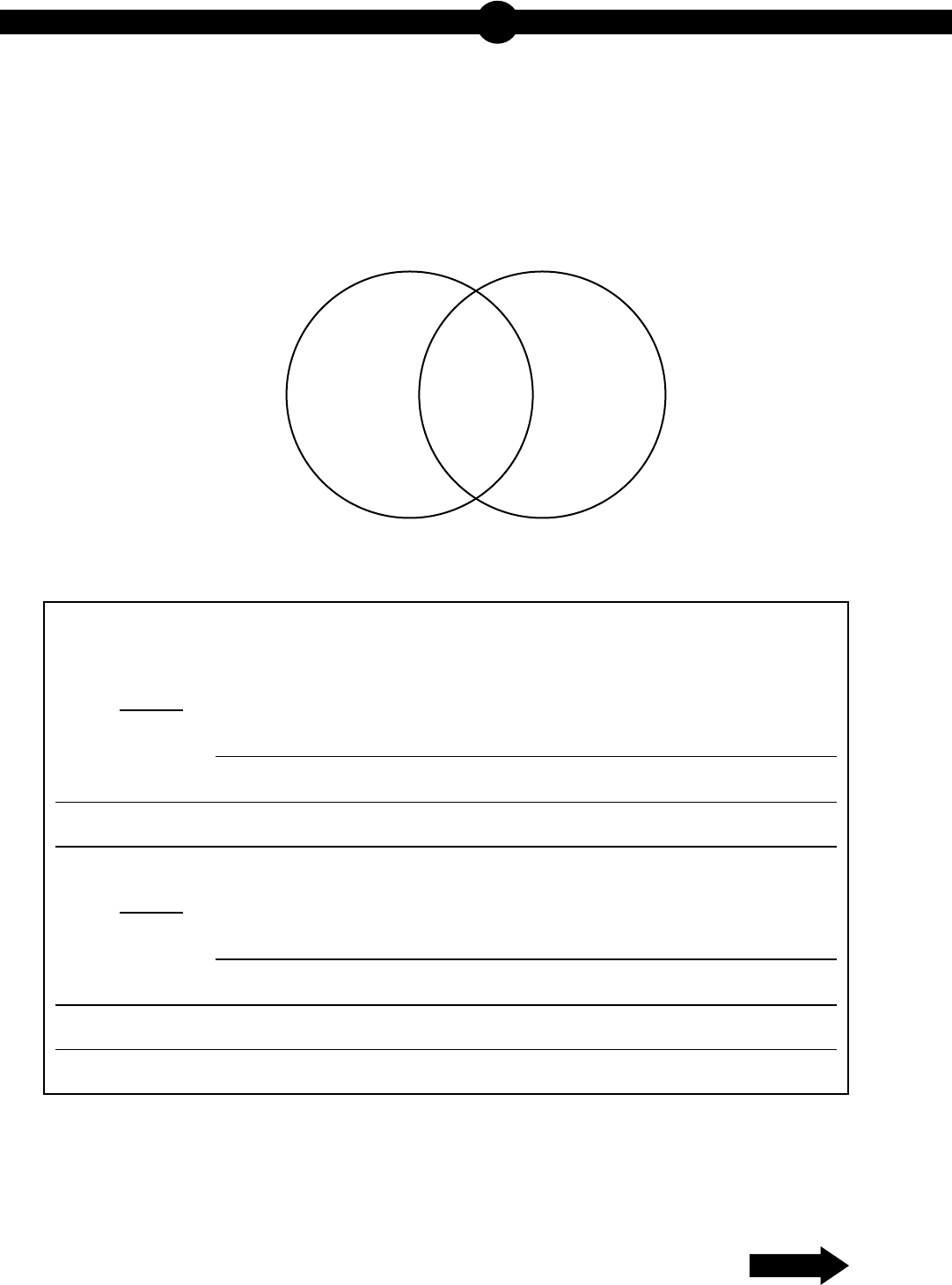
15. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
photosynthesis cellular respiration
area X area Zarea Y
Two Cellular Processes
A student draws a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two cellular processes.
Part A: Select two areas from the Venn diagram and describe a characteristic that
could be placed into each of the areas.
Area:
Characteristic:
Area:
Characteristic:
x
Converts light energy from the sun into
chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Z
Occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic
cells
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
35
1
BiologyMODULE1
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Some organisms would need to perform both
cellular respiration and photosynthesis because
photosynthesis is the only way those organisms could
obtain glucose, which is broken down during cellular
respiration in order to make ATP, which is necessary
for all cells and is not created in great enough
quantities during photosynthesis to be useful.
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of comparing and contrasting the basic transformation
of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two areas from the
Venn diagram and correctly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected areas (Area: X,
Characteristic: Converts light energy . . . into chemical energy in the form of glucose; Area: Z, Characteristic:
Occurs in the mitochondria). In Part B, the response correctly explains why some organisms would need to
perform both cellular respiration and photosynthesis (photosynthesis is the only way those organisms could
obtain glucose, which is broken down during cellular respiration in order to make ATP). The response is clear,
complete, and correct.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
36
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
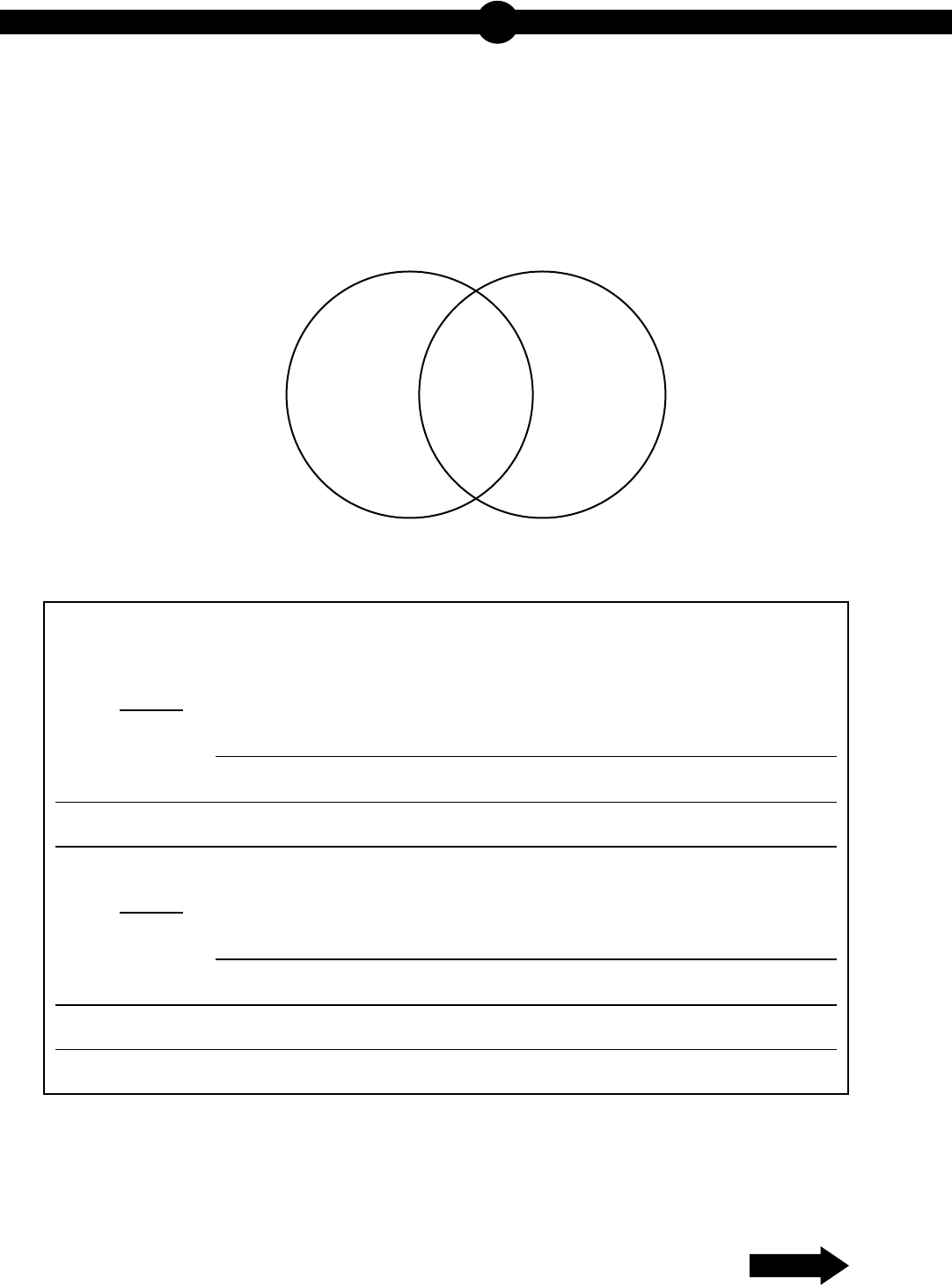
15. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
photosynthesis cellular respiration
area X area Zarea Y
Two Cellular Processes
A student draws a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two cellular processes.
Part A: Select two areas from the Venn diagram and describe a characteristic that
could be placed into each of the areas.
Area:
Characteristic:
Area:
Characteristic:
x
requires sunlight and can only ocur in
plants.
Y
Both photosynthesis and celular
respiration are proces’s that are used to obtain
energy.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
37
1
BiologyMODULE1
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
An organism might not have al the resources it
neds to do one of the proces’s so it does both. For
example, if a plant can’t complete photosynthesis
because of a lack of sunlight, it might finish of by
using celular respiration.
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting the basic transformation
of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two areas from the
Venn diagram and correctly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected areas (Area: X,
Characteristic: requires sunlight OR can only occur in plants; Area: Y, Characteristic: Both . . . are used to obtain
energy). In Part B, the response incorrectly explains why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis (lack of sunlight) and does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
38
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
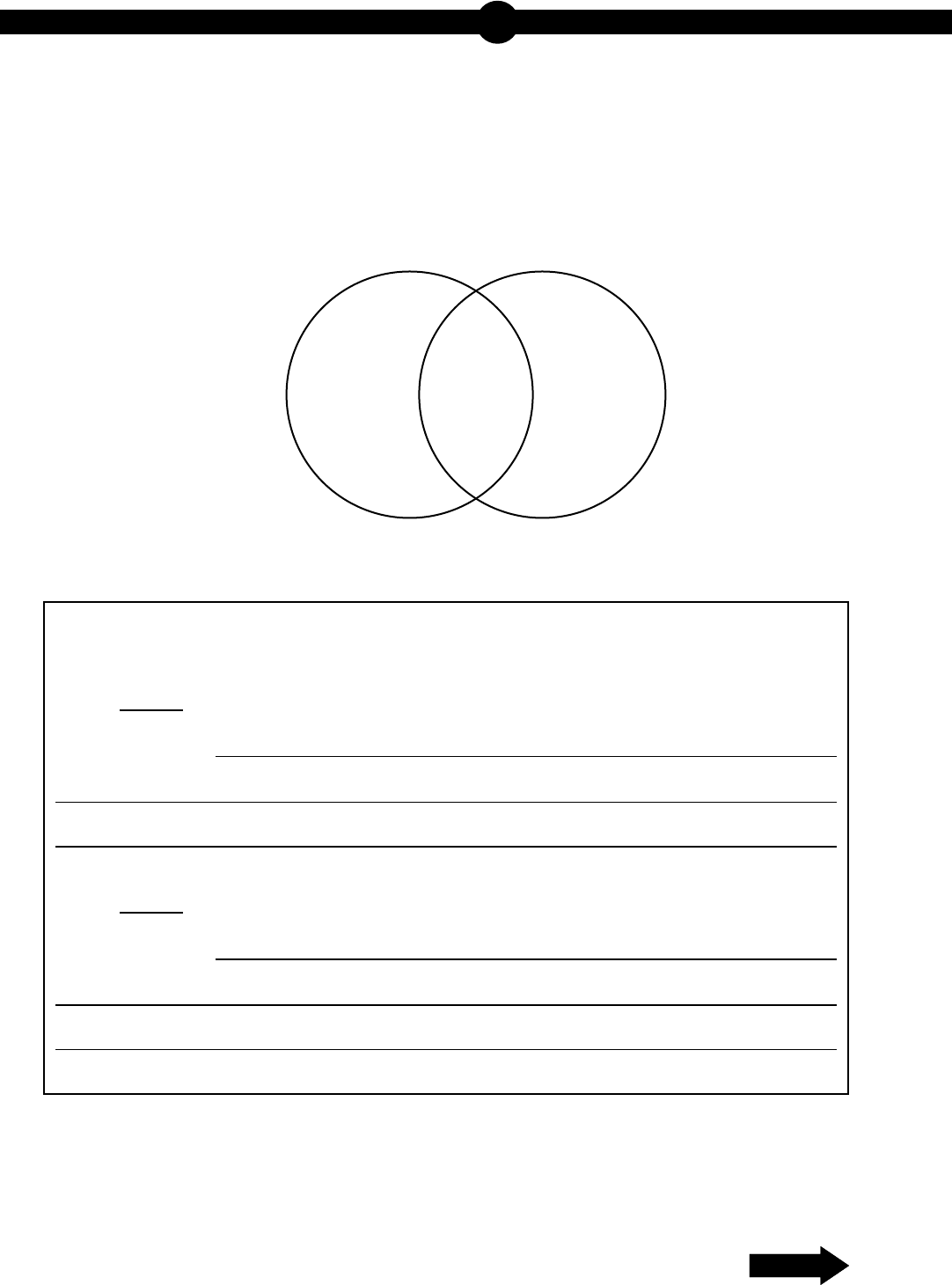
15. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
photosynthesis cellular respiration
area X area Zarea Y
Two Cellular Processes
A student draws a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two cellular processes.
Part A: Select two areas from the Venn diagram and describe a characteristic that
could be placed into each of the areas.
Area:
Characteristic:
Area:
Characteristic:
x
Y
2
2
O
2
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
39
1
BiologyMODULE1
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting the basic transformation
of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two areas from the
Venn diagram and correctly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected areas (Area: X,
Characteristic: requires sunlight OR only occur in plants; Area: Y, Characteristic: Both…are used to obtain
energy). In Part B, the response incorrectly explains why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis (lack of sunlight) and does not receive any credit.
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of comparing and contrasting the basic transformation
of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two areas from the
Venn diagram and incorrectly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected areas (Area:X,
Characteristic: occurs in the mitochondria; Area: Y, Characteristic: Both . . . involve light energy), so it does
not receive any credit. In Part B, the response correctly explains why some organisms would need to perform
both cellular respiration and photosynthesis (To acquire certain nutrients like glucose, organisms need to
photosynthesize. Then to make ATP, those organisms would use that glucose as one of the reactants in cellular
respiration).
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
40
1
BiologyMODULE1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
15. Use the diagram below to answer the question.
photosynthesis cellular respiration
area X area Zarea Y
Two Cellular Processes
A student draws a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two cellular processes.
Part A: Select two areas from the Venn diagram and describe a characteristic that
could be placed into each of the areas.
Area:
Characteristic:
Area:
Characteristic:
Y
Require light to take place
X
Plants only way of producing energy
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
41
1
BiologyMODULE1
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Some organisms perform both because they need the
extra energy to survive in maybe a harsher climate/
environment.
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of comparing and contrasting the basic transformation
of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two areas from the
Venn diagram and correctly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected areas (Area: X,
Characteristic: requires sunlight OR only occur in plants; Area: Y, Characteristic: Both…are used to obtain
energy). In Part B, the response incorrectly explains why some organisms would need to perform both cellular
respiration and photosynthesis (lack of sunlight) and does not receive any credit.
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of comparing and contrasting the
basic transformation of energy during photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Part A, the response selects two
areas from the Venn diagram and incorrectly describes a characteristic that could be placed into the selected
areas (Area: Y, Characteristic: Require light; Area: X, Characteristic: Plants only way of producing energy), so
it does not receive any credit. In Part B, the response incorrectly explains why some organisms would need to
perform both cellular respiration and photosynthesis (need energy to survive in a harsh climate/environment) and
does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
42
1
BiologyMODULE1
BIOLOGY MODULE 1—SUMMARY DATA
MULTIPLE-CHOICE
Sample
Number
Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 BIO.A.1.1.1 A 2 56% 23% 12% 9%
2
BIO.A.1.1.1 D 2 16% 17% 12% 55%
3
BIO.A.1.2.2 B 2 7% 62% 10% 21%
4
BIO.A.2.2.2 C 2 11% 13% 67% 9%
5
BIO.A.2.3.2 A 2 42% 25% 18% 14%
6
BIO.A.3.2.2 D 2 6% 7% 9% 79%
7
BIO.A.3.2.1 C 2 10% 7% 76% 8%
8 BIO.A.3.1.1 B 2 12% 59% 18% 11%
9
BIO.A.4.1.3 C 2 12% 17% 60% 11%
10 BIO.A.4.2.1 A 2 72% 7% 13% 8%
11
BIO.A.2.2.1 C 2 12% 5% 71% 12%
12 (P) BIO.A.2.1.1 D 2 16% 15% 18% 51%
13 (P) BIO.A.3.2.2 A 2 41% 27% 15% 17%
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE
Sample
Number
Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge
Mean Score
14 BIO.A.1.2.1 3 3 1.41
15 BIO.A.3.2.1 3 3 1.39

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
43
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
44
2
BiologyMODULE2
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEMS
1. Which event describes cellular activities that would be observed during cytokinesis in an
animalcell?
A. The cytoplasm of the parent cell divides following the division of the nucleus.
B. The chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle in their most tightly condensed
form.
C. The DNA and proteins condense and the centrioles move toward the opposite ends of the
cell to form a spindle.
D. The spindle fibers, attached to the two sister chromatids of each chromosome, contract
and separate as the chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.1.1.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 50% (correct answer)
p-value B 11%
p-value C 17%
p-value D 22%
Option Annotations A. Key: This is what happens during cytokinesis.
B. This activity occurs during metaphase.
C. These activities occur during prophase.
D. These activities occur during anaphase.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
45
2
BiologyMODULE2
2. A scientist wants to make a change to a genetic code that will lead to the removal of one amino
acid from the sequence of a protein. Which genetic material should the scientist remove?
A. three genes
B. three alleles
C. three nucleotides
D. three chromosomes
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.1.2.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 3
p-value A 15%
p-value B 21%
p-value C 53% (correct answer)
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations A. A gene is a segment of DNA.
B. An allele is a version of a gene.
C. Key: Removing three nucleotides would remove one amino acid
because a single amino acid is determined by a codon, and a
codon is three adjacent nucleotides.
D. A chromosome is a long DNA molecule.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
46
2
BiologyMODULE2
3. A specific genetic disorder is caused by nondisjunction. Which statement describes how the
genetic disorder occurs?
A. A problem with RNA replication leads to gametes with extra chromosomes.
B. A problem with chromosome separation leads to gametes with damaged chromosomes.
C. Incomplete DNA replication leads to gametes with half the usual number of chromosomes.
D. Incomplete chromosome separation leads to gametes with an abnormal number of
chromosomes.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.1.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 18%
p-value B 17%
p-value C 19%
p-value D 45% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. Nondisjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate.
B. Nondisjunction results in an abnormal number of chromosomes,
not damaged chromosomes.
C. Incomplete DNA replication is not involved in nondisjunction;
instead, the chromosomes fail to separate.
D. Key: Nondisjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to
separate, and the resulting daughter cells have an abnormal
number of chromosomes.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
47
2
BiologyMODULE2
4. Which sequence of events correctly describes the process of protein synthesis?
A. DNA transcription mRNA translation proteins produced
B. DNA translation mRNA transcription proteins produced
C. mRNA transcription polypeptides form translation proteins produced
D. mRNA
translation polypeptides form transcription proteins produced
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 45% (correct answer)
p-value B 29%
p-value C 14%
p-value D 12%
Option Annotations A. Key: The process of protein synthesis includes DNA being
transcribed into mRNA, which is translated into proteins.
B. Transcription occurs before translation in the production of proteins
within the cell.
C. Transcription produces mRNA, which is then translated to form
polypeptide chains.
D. Transcription occurs when DNA is used to make mRNA, before
translation occurs.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
48
2
BiologyMODULE2
5. A mutation present in a parent’s genetic code impacts offspring. Which statement most likely
describes the mutation?
A. The mutation can be recognized and repaired by enzymes.
B. The mutation is observed in the somatic cells of the parent.
C. The mutation changes a base without changing an amino acid.
D. The mutation alters the function of the protein made by the gene.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.1.3
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 10%
p-value B 18%
p-value C 17%
p-value D 56% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. If a repair enzyme were involved, then the mutation would not be
observed in the offspring.
B. Mutations in somatic cells are not passed to offspring.
C. If the mutation changes a base without changing an amino acid,
then the mutation is silent and would not affect the offspring.
D. Key: The mutation changes the sequence of bases and prevents
the protein from working properly.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
49
2
BiologyMODULE2
6. Use the list below to answer the question.
Scientific Evidence
1. Some genes from the bacteriumE. colihave sequences that are similar to genes found in
humans.
2. In the 1940s, infections by the bacteriumStaphylococcus aureuscould be treated
successfully with penicillin. Today, populations exist that are completely resistant to
natural penicillin.
3. Whales have tiny bones inside the rear portion of their bodies that are very similar to the
bones found in vertebrate legs.
4. Human embryos have gill slits similar to those observed in fish embryos.
Four pieces of evidence collected by scientists are listed. How did the scientists most likely use
these pieces of evidence?
A. to support the cell theory
B. to support thetheory of evolution
C. to explain the process of DNA replication
D. to explain the process of genetic mutations
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 3
p-value A 8%
p-value B 72% (correct answer)
p-value C 6%
p-value D 13%
Option Annotations A. Cell theory would be supported with evidence of living things being
made of cells.
B. Key: Genetic code, natural selection, and anatomical and
embryological similarities are all evidence for the theory of
evolution.
C. Genetic code, natural selection, and anatomical and embryological
similarities are all evidence for the theory of evolution and do not
explain how DNA molecules are copied.
D. Genetic code, natural selection, and anatomical and embryological
similarities are all evidence for the theory of evolution and do not
explain how permanent changes to DNA occur.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
50
2
BiologyMODULE2
7. A scientist determined that the average air temperature in an area increased during an observed
period of time. The area included several small ponds. Which change to the water cycle
mostlikely occurred in the area during the observed period of time?
A. runoff decreased
B. evaporation increased
C. precipitation decreased
D. condensation increased
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.3
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 7%
p-value B 61% (correct answer)
p-value C 19%
p-value D 14%
Option Annotations A. A decrease in runoff cannot be determined without measuring
precipitation amounts.
B. Key: Evaporation most likely increased because the temperature
increase caused an increase in the kinetic energy of the water
molecules.
C. There is no evidence presented to suggest a change in the amount
of precipitation.
D. The humidity of the air is not described, so condensation amounts
cannot be determined.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
51
2
BiologyMODULE2
8. A student made an observation about a plant. Which statement is an observation that the
student most likely made?
A. Plants benefit from tilting their leaves toward the Sun.
B. At 10 a.m. the plant’s leaves were tilted toward the Sun.
C. Plants that do not tilt their leaves toward the Sun will not survive.
D. The tilting of plant leaves toward the Sun evolved over a long period of time.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.3.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 28%
p-value B 54% (correct answer)
p-value C 8%
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations A. This is an inference the student could make based on multiple
observations of plants; it is not an observation.
B. Key: The student can use the sense of sight to see that the plant is
tilted at a specific time.
C. This is a hypothesis that could be tested; it is not information that is
directly noticed by the senses.
D. This is a theory, which relies on a set of scientific principles
to explain a phenomena and cannot be formed from a single
observation.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
52
2
BiologyMODULE2
9. Oak treehoppers are parasites of trees. Which statement describes the relationship between an
oak treehopper and a tree?
A. Both the oak treehopper and the tree are harmed by one another.
B. The oak treehopper benefits from the tree, while the tree is unaffected.
C. The tree benefits from the oak treehopper, while the oak treehopper is unaffected.
D. The oak treehopper benefits from the tree, while the tree is harmed by the oak treehopper.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 5%
p-value B 14%
p-value C 7%
p-value D 74% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. This describes a mutually negative relationship and not a parasitic
relationship, in which one organism benefits and the other organism
is harmed.
B. This describes commensalism, a relationship in which one
organism benefits and the other organism is unaffected.
C. This describes commensalism, a relationship in which one
organism benefits and the other organism is unaffected.
D. Key: In a parasitic relationship, one organism is harmed by another
organism, the parasite, which benefits.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
53
2
BiologyMODULE2
10. Some scientists believe that a gradual but steady atmospheric warming has led to changes
in the reproductive rates of several moth and butterfly species in a region. These species are
producing multiple generations in one year, rather than the single generation per year they
have historically produced. Which statement describes the most likely impact of the additional
generations on the ecosystem in this region?
A. Insects will have less ability to develop genetic resistance to insecticides.
B. Insect predator populations will increase due to increased availability of prey.
C. Plants pollinated by insects will have less of a chance of producing offspring.
D. Plant and animal diversity will increase as more insects are produced each year.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.4
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 10%
p-value B 59% (correct answer)
p-value C 9%
p-value D 22%
Option Annotations A. Genetic resistance would increase only if a beneficial gene for
resistance were passed on to offspring.
B. Key: The insect population will increase, which will make a food
resource more readily available for predators and result in an
increase in the predator population.
C. Plants that benefit from the pollinators would experience increased
pollination because of the increase in the insect population.
D. Plant and animal diversity depends on natural selection, not on an
increase in the number of insects.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
54
2
BiologyMODULE2
11. Photosynthesis is a process that helps cycle matter through the environment. Which statement
best explains the role of photosynthesis in the carbon cycle?
A. Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air, and carbohydrates are produced.
B. Carbon dioxide is released into the air, and carbohydrates are broken down.
C. Carbon and nitrogen are absorbed into the soil, and carbohydrates are produced.
D. Carbon and nitrogen are released from the soil, and carbohydrates are broken down.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.3
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 48% (correct answer)
p-value B 26%
p-value C 15%
p-value D 10%
Option Annotations A. Key: Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and use sunlight
to produce chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of
carbohydrates.
B. In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air, not
released, and carbohydrates are produced, not broken down.
C. In photosynthesis, carbon is absorbed as carbon dioxide gas from
the air, not from elemental carbon in the soil.
D. Elemental carbon and nitrogen are not produced by
photosynthesis, and carbohydrates are produced in the form of
glucose.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
55
2
BiologyMODULE2
Directions: Use the information presented on page 55 to answer questions12 and13.
A New Fossil Discovery
Geologists have recently unearthed fossils of a species that could provide the evolutionary link
between arthropods such as insects, spiders, and lobsters. The fossils are in a deposit called the
Burgess Shale, in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia. The Burgess Shale is one of the most
abundant fossil deposits in the world, and it provides scientists withinformation about the middle
Cambrian period, which was approximately 508 million years ago.
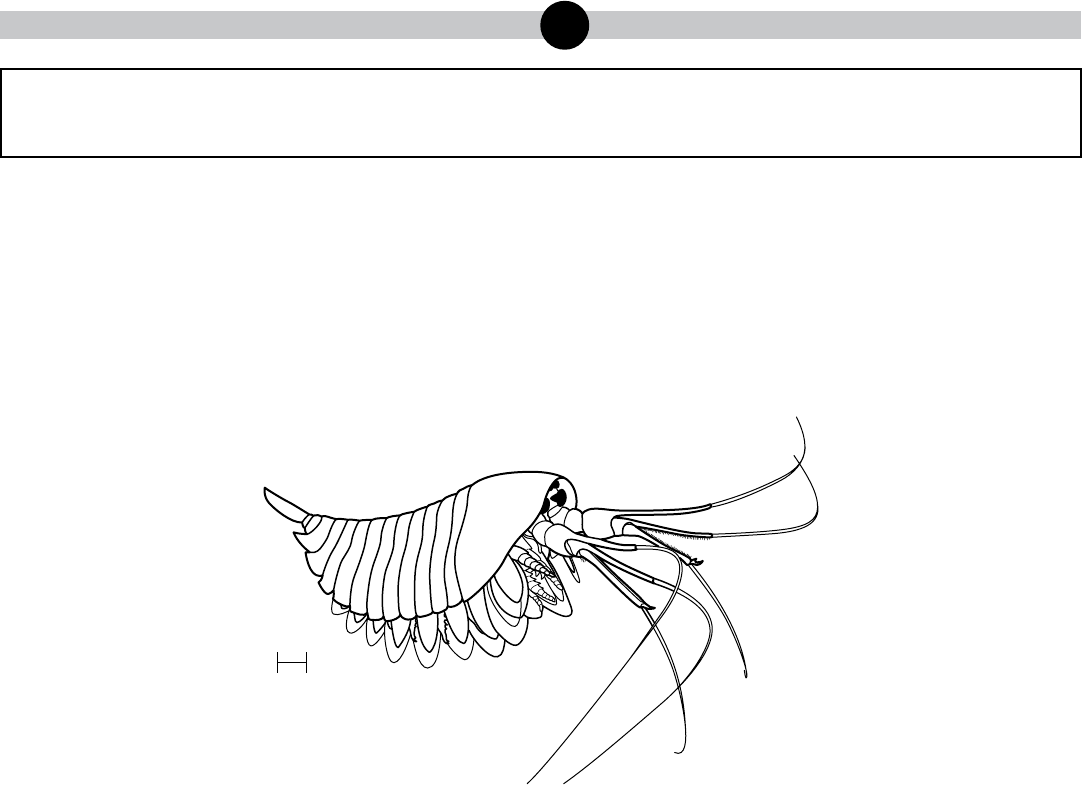
Yawunik
1 cm
The fossilized organism, identified as Yawunik, was equipped with three longclaws, two of which
had opposing rows of teeth to better grip prey. These multipurpose appendages, which would
have been opened to capture prey, could be pulled in close to the body to reduce drag while
swimming. The organism had the features of an arthropod: external skeleton, segmented body, and
jointed appendages. However, it did not have the advanced traits present in other similar groups
of organisms that have survived until the present day. The discovery of 42 fossil specimens at one
location suggests Yawunik was common during the deposition of the Burgess Shale.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
56
2
BiologyMODULE2
12. Which statement best describes how scientists use the Yawunik fossil evidence to support its
evolutionary relationship to other arthropods?
A. They interpret the similar anatomy of other arthropods.
B. They identify the DNA of several other similar arthropods.
C. They locate other arthropod fossils in the Burgess Shale area.
D. They compare embryological development to other arthropods.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 59% (correct answer)
p-value B 13%
p-value C 13%
p-value D 15%
Option Annotations A. Key: The scientists compared the anatomical and structural
similarities to modern arthropods and other arthropod fossils.
B. The scientists used anatomical comparisons and did not
demonstrate the use of DNA fingerprinting techniques to compare
genetic material.
C. Locating other arthropods does not show an evolutionary
relationship.
D. The scientists used anatomical comparisons and did not
demonstrate the use of comparing different embryos of organisms
that were similar.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
57
2
BiologyMODULE2
13. Which statement describes how the Yawunik most likely interacted with other organisms in its
environment?
A. It competed with producers for sunlight.
B. It had a mutualistic relationship with phytoplankton.
C. It lived symbiotically with most small aquatic organisms.
D. It was a predator that obtained energy from other consumers.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 5%
p-value B 8%
p-value C 25%
p-value D 61% (correct answer)
Option Annotations A. The arthropod was not a plant, so it did not produce its own energy.
B. The evidence of teeth and claws to grip prey demonstrate that it
was a predator that consumed organisms.
C. The evidence of teeth and claws to grip prey demonstrate that it
was a predator that consumed organisms.
D. Key: The evidence of teeth and claws to grip prey demonstrate that
it was a predator that consumed other consumers and not plants.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
58
2
BiologyMODULE2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
14. A group of students went to a local park. When the students returned to their classroom, they
were asked to describe what they saw.
Student Statement 1: There were fourteen trees in the park; all were the same species.
Student Statement 2: There were no weeds in the park, so pesticides must have been used.
Student Statement 3: More birds would come to the park if feeding stations were added.
Forms of Scientific Information
• fact
• hypothesis
• inference
• observation
• law
• principle
• theory
Part A: Select two student statements, and classify each of them as one form of
scientific information.
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
59
2
BiologyMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain how an observation and a scientific law are related.
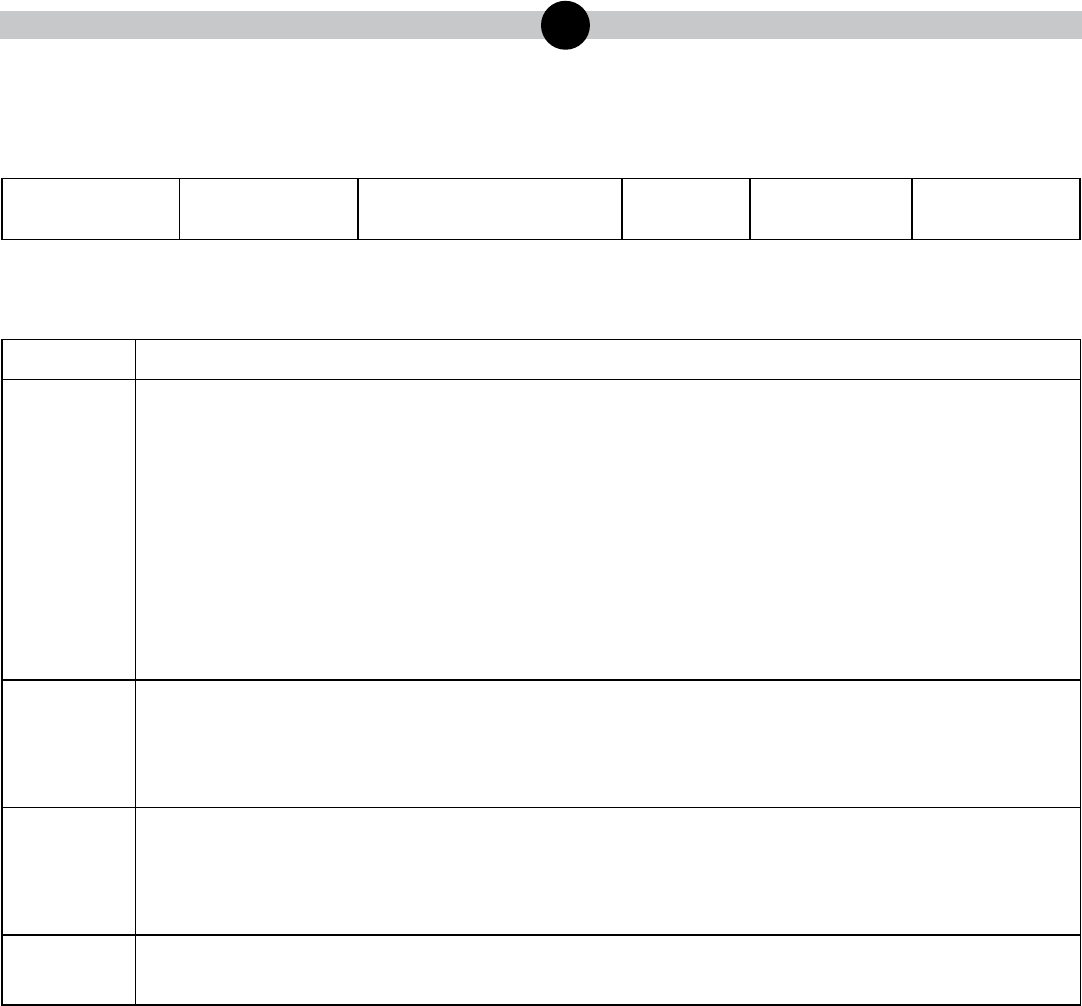
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
60
2
BiologyMODULE2
SCORING GUIDE
#14 Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.3.1 Depth of Knowledge 3 Mean Score 1.66
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to distinguish
among the scientific terms hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and
observationby
• classifying one statement as a particular type of scientific information,
AND
• classifying a second statement as a particular type of scientific information,
AND
• explaining how an observation and a scientific law are related.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how to distinguish among the
scientific terms hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation by
fulfilling two of the bullets under the 3-point response. The response may contain
some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how to distinguish among
the scientific terms hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation
by fulfilling one of the bullets listed under the 3-point response. The response may
contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
concept being tested.
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
61
2
BiologyMODULE2
Responses That Will Receive Credit
Part A (2 points total; 1 point for classifying each of two statements):
• Statement 1: observation
OR
• Statement 1: fact
• Statement 2: inference
• Statement 3: hypothesis
Part B (1 point):
• An observation might lead a scientist to carry out research that, along with the research of
many other scientists, discovers and confirms a scientific law.
OR
• A scientific law might describe or explain a phenomenon that a person can see and about
which an observation can be made.
OR
• A person might make an observation, such as the falling of a dropped object, that can be
explained by a scientific law.
Background Information:
• An observation is simply some occurrence that a person notices with senses.
• An inference is a possible explanation for the observation.
• A hypothesis is a tentative answer to a well-framed question or an explanation that can be
tested by an experiment. The results of the experiment may either support the hypothesis
or disprove it. A hypothesis is a limited explanation of some phenomenon.
• A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world
that has been repeatedly tested and confirmed through experimentation.
• A scientific law is an accurate description of a natural phenomenon. A law does not explain
the phenomenon; a theory does explain it.
• A scientific principle is considered by most to be the same as a scientific law.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
62
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
14. A group of students went to a local park. When the students returned to their classroom, they
were asked to describe what they saw.
Student Statement 1: There were fourteen trees in the park; all were the same species.
Student Statement 2: There were no weeds in the park, so pesticides must have been used.
Student Statement 3: More birds would come to the park if feeding stations were added.
Forms of Scientific Information
• fact
• hypothesis
• inference
• observation
• law
• principle
• theory
Part A: Select two student statements, and classify each of them as one form of
scientific information.
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
1
observation
2
inference

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
63
2
BiologyMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain how an observation and a scientific law are related.
1
Fact
2
Hypothesis
Observations support a scientific law and
further prove that it is correct. Observations
made by a scientist may lead them to a
hypothesis and experiments that create a
scientific law.
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to distinguish among the scientific terms
hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation. In Part A, the response correctly classifies
two selected statements as particular types of scientific information (Student Statement Number: 1,
Classification:observation; Student Statement Number: 2, Classification: inference). In Part B, the response
correctly explains how an observation and a scientific law are related (Observations support a scientific
law and further prove that it is correct). The response also correctly phrased this relationship a second way
(Observations...may lead them to a hypothesis and experiments that create a scientific law). The response is
clear, complete, and correct.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
64
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
14. A group of students went to a local park. When the students returned to their classroom, they
were asked to describe what they saw.
Student Statement 1: There were fourteen trees in the park; all were the same species.
Student Statement 2: There were no weeds in the park, so pesticides must have been used.
Student Statement 3: More birds would come to the park if feeding stations were added.
Forms of Scientific Information
• fact
• hypothesis
• inference
• observation
• law
• principle
• theory
Part A: Select two student statements, and classify each of them as one form of
scientific information.
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
1
ft
3
w

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
65
2
BiologyMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain how an observation and a scientific law are related.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Aoeaotneso phi
a sr a l
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how to distinguish among the scientific terms hypothesis,
inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation. In Part A, the response correctly classifies only one
selected statement as a particular type of scientific information (Student Statement Number: 1, Classification:
fact). The second chosen statement and classification (Student Statement Number: 3, Classification: law) is
incorrect and does not receive any credit. In Part B, the response correctly explains how an observation and a
scientific law are related (An observation then leads to a hypothesis and research leads to a law).
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
66
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
14. A group of students went to a local park. When the students returned to their classroom, they
were asked to describe what they saw.
Student Statement 1: There were fourteen trees in the park; all were the same species.
Student Statement 2: There were no weeds in the park, so pesticides must have been used.
Student Statement 3: More birds would come to the park if feeding stations were added.
Forms of Scientific Information
• fact
• hypothesis
• inference
• observation
• law
• principle
• theory
Part A: Select two student statements, and classify each of them as one form of
scientific information.
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
2
hypothesis
3
observation

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
67
2
BiologyMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain how an observation and a scientific law are related.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
A scientific law is a hypothesis that was proven true
through steps such as observation.
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how to distinguish among the scientific terms
hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation. In Part A, the response incorrectly
classifies two selected statements as particular types of scientific information (Student Statement Number: 2,
Classification:hypothesis; Student Statement Number: 3, Classification: observation) and does not receive any
credit. In Part B, the response correctly explains how an observation and a scientific law are related (scientific
law . . . was proven true through steps such as observation).
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
68
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
14. A group of students went to a local park. When the students returned to their classroom, they
were asked to describe what they saw.
Student Statement 1: There were fourteen trees in the park; all were the same species.
Student Statement 2: There were no weeds in the park, so pesticides must have been used.
Student Statement 3: More birds would come to the park if feeding stations were added.
Forms of Scientific Information
• fact
• hypothesis
• inference
• observation
• law
• principle
• theory
Part A: Select two student statements, and classify each of them as one form of
scientific information.
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Student Statement Number:
Classification:
Go to the next page to finish question 14.
GO ON
3
observation
2
hypothesis

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
69
2
BiologyMODULE2
14. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part B: Explain how an observation and a scientific law are related.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
They are related because they both have information that
needs to be viewed over and over also it’s based off of a
outcome
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of how to distinguish among
the scientific terms hypothesis, inference, law, theory, principle, fact, and observation. In Part A, the response
incorrectly classifies two selected statements as particular types of scientific information (Student Statement
Number:3, Classification: observation; Student Statement Number: 2, Classification: hypothesis) and does not
receive any credit. In Part B, the response incorrectly explains how an observation and a scientific law are related
(both have information that needs to be viewed over and over) and does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
70
2
BiologyMODULE2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
15. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Second Position
First Position
U
U
CAG
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third Position
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
AUU
AUC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
GCU
GCC
GCA
GCG
Ala
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
Tyr
stop
stop
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
Asn
Lys
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
Cys
stop
Trp
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
GGU
GGC
GGA
GGG
Gly
Ser
Arg
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
RNA Codon Chart
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
GAU
GAC
GAA
GAG
Asp
Glu
A scientist was studying a long protein in a cell. The amino acid leucine (Leu) was observed in
the middle of the protein. Further testing revealed that the codon UUA codes for the leucine.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
71
2
BiologyMODULE2
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part A: Provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that
would not result in a phenotypic change to the cell.
Part B: Provide an example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of the leucine
codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the
middle of the protein.
Part C: Explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the
protein would likely have on the function of the protein.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
72
2
BiologyMODULE2
SCORING GUIDE
#15 Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.3.1 Depth of Knowledge 3 Mean Score 1.37
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how genetic mutations alter
the DNA sequence and may or may not affect phenotype by
• providing an example of a mutation to a codon that would not result in a
phenotypic change to the cell,
AND
• providing an example of a mutation to a UUA codon that would create a stop
codon,
AND
• explaining what effect a single base deletion would have on the encoded
protein.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how genetic mutations alter the
DNA sequence and may or may not affect phenotype by fulfilling two of the bullets
under the 3-point response. The response may contain some work that is incomplete
or unclear.
1
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how genetic mutations alter
the DNA sequence and may or may not affect phenotype by fulfilling one of the bullets
listed under the 3-point response. The response may contain some work that is
incomplete or unclear.
0
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
concept being tested.
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
73
2
BiologyMODULE2
Responses That Will Receive Credit
Part A (1 point):
• If the UUA leucine codon were changed to UUG, this would not cause a phenotypic
change.
OR
• If the UUA leucine codon were changed to CUU, CUC, CUA, or CUG, this would not cause
a phenotypic change.
Part B (1 point):
• If the UUA leucine codon were changed to UGA, this would create a stop codon in the
middle of the gene.
OR
• If the UUA leucine codon were changed to UAA, this would create a stop codon in the
middle of the gene.
Part C (1 point):
• Deleting a single base from a gene would result in all the codons after the deletion being
different, so the protein would have the wrong amino acid sequence and would not
function.
OR
• Deleting a single base from a gene is a frameshift mutation; the reading frame is shifted,
and the encoded protein would not function.
OR
• If a single base is deleted from a gene, then every amino acid after that deletion would be
wrong and there might be a stop codon created, so the protein would not work.
Background Information:
• For Part A, these mutations cause no phenotypic change because the new codons still
code for leucine.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
74
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 3 points
15. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Second Position
First Position
U
U
CAG
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third Position
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
AUU
AUC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
GCU
GCC
GCA
GCG
Ala
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
Tyr
stop
stop
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
Asn
Lys
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
Cys
stop
Trp
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
GGU
GGC
GGA
GGG
Gly
Ser
Arg
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
RNA Codon Chart
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
GAU
GAC
GAA
GAG
Asp
Glu
A scientist was studying a long protein in a cell. The amino acid leucine (Leu) was observed in
the middle of the protein. Further testing revealed that the codon UUA codes for the leucine.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
75
2
BiologyMODULE2
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part A: Provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that
would not result in a phenotypic change to the cell.
Part B: Provide an example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of the leucine
codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the
middle of the protein.
A p mn a c U A w i a
s c.
Part C: Explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the
protein would likely have on the function of the protein.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
A p mn a ss h c o U U
w o c a pp c.
Dg s w c a f-s mn n
m h e p. l b a h d
o w v o, ce ag h p’s
fn.
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how genetic mutations alter the DNA sequence and
how they may or may not affect phenotype. In Part A, the response provides a correct example of a mutation
to the leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a phenotype change to the cell (A point mutation that
switches the codon from UUA to UUG). In Part B, the response provides a correct example of a mutation to a
single nucleotide of the leucine codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the middle of
the protein (A point mutation that changes UUA to UAA). In Part C, the response correctly explains what effect
deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the protein would likely have on the function of the protein
(Deleting a base would cause a frame-shift mutation . . . completely altering the protein’s function). The response
is clear, complete, and correct.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
76
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 2 points
15. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Second Position
First Position
U
U
CAG
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third Position
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
AUU
AUC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
GCU
GCC
GCA
GCG
Ala
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
Tyr
stop
stop
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
Asn
Lys
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
Cys
stop
Trp
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
GGU
GGC
GGA
GGG
Gly
Ser
Arg
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
RNA Codon Chart
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
GAU
GAC
GAA
GAG
Asp
Glu
A scientist was studying a long protein in a cell. The amino acid leucine (Leu) was observed in
the middle of the protein. Further testing revealed that the codon UUA codes for the leucine.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
77
2
BiologyMODULE2
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part A: Provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that
would not result in a phenotypic change to the cell.
Part B: Provide an example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of the leucine
codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the
middle of the protein.
AemodeAA
Part C: Explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the
protein would likely have on the function of the protein.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
T d Aodoru
pnychge
Iy leailber ee u
cssehg aptn
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how genetic mutations alter the DNA sequence and how
they may or may not affect phenotype. In Part A, the response provides a correct example of a mutation to the
leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a phenotype change to the cell (codon CUA would not result in
a phenotypic change). In Part B, the response provides a correct example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of
the leucine codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the middle of the protein (UAA).
In Part C, the response does not correctly explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for
the protein would likely have on the function of the protein (cause some changes to that protein) and does not
receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
78
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 1 point
15. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Second Position
First Position
U
U
CAG
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third Position
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
AUU
AUC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
GCU
GCC
GCA
GCG
Ala
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
Tyr
stop
stop
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
Asn
Lys
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
Cys
stop
Trp
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
GGU
GGC
GGA
GGG
Gly
Ser
Arg
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
RNA Codon Chart
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
GAU
GAC
GAA
GAG
Asp
Glu
A scientist was studying a long protein in a cell. The amino acid leucine (Leu) was observed in
the middle of the protein. Further testing revealed that the codon UUA codes for the leucine.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
79
2
BiologyMODULE2
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part A: Provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that
would not result in a phenotypic change to the cell.
Part B: Provide an example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of the leucine
codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the
middle of the protein.
UAG
Part C: Explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the
protein would likely have on the function of the protein.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
CUC
It can completely change the codon.
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how genetic mutations alter the DNA sequence and how
they may or may not affect phenotype. In Part A, the response provides a correct example of a mutation to the
leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a phenotype change to the cell (CUC). In Part B, the response
does not provide a correct example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a
phenotype change to the cell (UAG) and does not receive any credit. In Part C, the response does not correctly
explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the protein would likely have on the
function of the protein (completely change the codon) and does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
80
2
BiologyMODULE2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Response Score: 0 points
15. Use the chart below to answer the question.
Second Position
First Position
U
U
CAG
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
U
C
A
G
Third Position
UUU
UUC
UUA
UUG
Phe
Leu
CUU
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
GUU
GUC
GUA
GUG
Val
AUU
AUC
AUA
AUG
Ile
Met
CCU
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
GCU
GCC
GCA
GCG
Ala
UAU
UAC
UAA
UAG
Tyr
stop
stop
His
Gln
CAU
CAC
CAA
CAG
Asn
Lys
AAU
AAC
AAA
AAG
Cys
stop
Trp
UGU
UGC
UGA
UGG
CGU
CGC
CGA
CGG
Arg
GGU
GGC
GGA
GGG
Gly
Ser
Arg
AGU
AGC
AGA
AGG
RNA Codon Chart
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
Ser
ACU
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
GAU
GAC
GAA
GAG
Asp
Glu
A scientist was studying a long protein in a cell. The amino acid leucine (Leu) was observed in
the middle of the protein. Further testing revealed that the codon UUA codes for the leucine.
Go to the next page to finish question 15.
GO ON

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
81
2
BiologyMODULE2
15. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Part A: Provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that
would not result in a phenotypic change to the cell.
Part B: Provide an example of a mutation to a single nucleotide of the leucine
codon in the cell that would cause a stop codon to be inserted into the
middle of the protein.
Part C: Explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the
protein would likely have on the function of the protein.
STOP
AFTER YOU HAVE CHECKED YOUR WORK, CLOSE YOUR ANSWER
BOOKLET AND TEST BOOKLET SO YOUR TEACHER WILL KNOW
YOU ARE FINISHED.
A silent mutation would not have any phenotypic
change to the cell
.
A translation would cause a stop codon to be
inserted into the middle of the protein
.
Deleting a single base from the gene that codes
the protein would cause a major mutation
.
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of how genetic mutations alter
the DNA sequence and how they may or may not affect phenotype. In Part A, the response does not provide an
example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a phenotype change to the cell (A
silent mutation would not have any phenotypic change) and does not receive any credit. In Part B, the response
does not provide an example of a mutation to the leucine codon in the cell that would not result in a phenotype
change to the cell (A translation would cause a stop codon) and does not receive any credit. In Part C, the
response does not correctly explain what effect deleting a single base from the gene that codes for the protein
would likely have on the function of the protein (cause a major mutation) and does not receive any credit.
Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
82
2
BiologyMODULE2
BIOLOGY MODULE 2—SUMMARY DATA
MULTIPLE-CHOICE
Sample
Number
Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 BIO.B.1.1.1 A 2 50% 11% 17% 22%
2 BIO.B.1.2.2 C 3 15% 21% 53% 11%
3 BIO.B.2.1.2 D 2 18% 17% 19% 45%
4 BIO.B.2.2.1 A 2 45% 29% 14% 12%
5 BIO.B.3.1.3 D 2 10% 18% 17% 56%
6 BIO.B.3.2.1 B 3 8% 72% 6% 13%
7 BIO.B.4.2.3 B 2 7% 61% 19% 14%
8 BIO.B.3.3.1 B 2 28% 54% 8% 9%
9 BIO.B.4.2.2 D 2 5% 14% 7% 74%
10 BIO.B.4.2.4 B 2 10% 59% 9% 22%
11 BIO.B.4.2.3 A 2 48% 26% 15% 10%
12 (P) BIO.B.3.2.1 A 2 59% 13% 13% 15%
13 (P) BIO.B.4.2.2 D 2 5% 8% 25% 61%
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE
Sample
Number
Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge
Mean Score
14 BIO.B.3.3.1 3 3 1.66
15 BIO.B.2.3.1 3 3 1.37

Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—August 2022
83
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.

Copyright © 2022 by the Pennsylvania Department of Education. The materials contained in
this publication may be duplicated by Pennsylvania educators for local classroom use. This
permission does not extend to the duplication of materials for commercial use.
Keystone Exams
Biology
Item and Scoring Sampler 2022
