
Pennsylvania Department of Education
Keystone Exams
Biology
Item and Scoring Sampler
2016–2017
Pennsylvania Department of Education Bureau of Curriculum, Assessment and Instruction—
September 2016

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
Introduction .................................................................1
About the Keystone Exams .....................................................1
Alignment ...............................................................1
Depth of Knowledge .......................................................2
Exam Format .............................................................2
Item and Scoring Sampler Format ................................................3
Biology Exam Directions .......................................................4
General Description of Scoring Guidelines for Biology ................................5
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Multiple-Choice Questions ......................................................6
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................20
Scoring Guide ...........................................................21
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................27
Scoring Guide ...........................................................28
Biology Module 1—Summary Data ..............................................35
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Multiple-Choice Questions .....................................................37
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................52
Scoring Guide ...........................................................53
Constructed-Response Item ...................................................60
Scoring Guide ...........................................................61
Biology Module 2—Summary Data ..............................................67

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
1
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
INTRODUCTION
The Pennsylvania Department of Education (PDE) provides districts and schools with tools to assist
in delivering focused instructional programs aligned to the Pennsylvania Core Standards. These tools
include the standards, assessment anchor documents, Keystone Exams Test Definition, Classroom
Diagnostic Tool, Standards Aligned System, and content-based item and scoring samplers. This
2016 Biology Item and Scoring Sampler is a useful tool for Pennsylvania educators in preparing
students for the Keystone Exams.
This Item and Scoring Sampler contains released operational multiple-choice and constructed-
response items that have appeared on previously administered Keystone Exams. These items will
not appear on any future Keystone Exams. Released items provide an idea of the types of items that
have appeared on operational exams and that will appear on future operational Keystone Exams.
Each item has been through a rigorous review process to ensure alignment with the Assessment
Anchors and Eligible Content. This sampler includes items that measure a variety of Assessment
Anchor or Eligible Content statements, but it does not include sample items for all Assessment
Anchor or Eligible Content statements.
The items in this sampler may be used as examples for creating assessment items at the classroom
level and may be copied and used as part of a local instructional program.
1
Classroom teachers
may find it beneficial to have students respond to the constructed-response items in this sampler.
Educators can then use the sampler as a guide to score the responses either independently or
together with colleagues.
ABOUT THE KEYSTONE EXAMS
The Keystone Exams are end-of-course assessments currently designed to assess proficiencies
in Algebra I, Biology, and Literature. For detailed information about how the Keystone Exams are
being integrated into the Pennsylvania graduation requirements, please contact the Pennsylvania
Department of Education or visit the PDE website at http://www.education.pa.gov.
Alignment
The Biology Keystone Exam consists of questions grouped into two modules: Module 1—Cells and
Cell Processes and Module 2—Continuity and Unity of Life. Each module corresponds to specific
content, aligned to statements and specifications included in the course-specific assessment anchor
documents. The Biology content included in the Keystone Biology multiple-choice questions will
align with the assessment anchors as defined by the Eligible Content statements. The process skills,
directives, and action statements will also specifically align with the Assessment Anchors as defined
by the Eligible Content statements.
The content included in Biology constructed-response items aligns with content included in the
Eligible Content statements. The process skills, directives, and action statements included in the
performance demands of the Biology constructed-response items align with specifications included
in the Assessment Anchor statements, the Anchor Descriptor statements, and/or the Eligible Content
statements. In other words, the verbs or action statements used in the constructed-response items
or stems can come from the Eligible Content, Anchor Descriptor, or Assessment Anchor statements.
1
The permission to copy and/or use these materials does not extend to commercial purposes.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
2
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
Depth of Knowledge
Webb’s Depth of Knowledge (DOK) was created by Dr. Norman Webb of the Wisconsin Center
for Education Research. Webb’s definition of depth of knowledge is the cognitive expectation
demanded by standards, curricular activities, and assessment tasks. Webb’s DOK includes four
levels, from the lowest (basic recall) level to the highest (extended thinking) level.
Depth of Knowledge
Level 1 Recall
Level 2 Basic Application of Skill/Concept
Level 3 Strategic Thinking
Level 4 Extended Thinking
Each Keystone item has been through a rigorous review process to ensure that it is as demanding
cognitively as what is required by the assigned Assessment Anchor as defined by the Eligible
Content. For additional information about depth of knowledge, please visit the PDE website at
http://static.pdesas.org/Content/Documents/Keystone_Exam_Program_Overview.PDF.
Exam Format
The Keystone Exams are delivered in a paper-and-pencil format as well as in a computer-based
online format. The multiple-choice questions require students to select the best answer from four
possible answer options and record their answers in the spaces provided. The correct answer for
each multiple-choice question is worth onepoint. The constructed-response items require students
to develop and write (or construct) their responses. Constructed-response items in Biology are
scored using item-specific scoring guidelines based on a 0–3-point scale. Each multiple-choice
question is designed to take about one minute to one-and-a-half minutes to complete. Each
constructed-response item is designed to take about eight minutes to complete. The estimated
time to respond to a test question is the same for both test formats. During an actual exam
administration, students are given additional time as necessary to complete the exam.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
3
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
ITEM AND SCORING SAMPLER FORMAT
This sampler includes the test directions and scoring guidelines that appear in the Keystone Exams.
Each sample multiple-choice question is followed by a table that includes the alignment, the answer
key, the DOK, the percentage
2
of students who chose each answer option, and a brief answer option
analysis or rationale. Each constructed-response item is followed by a table that includes the item
alignment, the DOK, and the mean student score. Additionally, each of the included item-specific
scoring guidelines is combined with sample student responses representing each score point to
form a practical, item-specific scoring guide. The General Description of Scoring Guidelines for
Biology used to develop the item-specific scoring guidelines should be used if any additional item-
specific scoring guidelines are created for use within local instructional programs.
Example Multiple-Choice Question Information Table
Item Information
Alignment Assigned AAEC
Answer Key Correct Answer
Depth of Knowledge Assigned DOK
p-value A Percentage of students who selected each option
p-value B Percentage of students who selected each option
p-value C Percentage of students who selected each option
p-value D Percentage of students who selected each option
Option Annotations Brief answer option analysis or rationale
Example Constructed-Response Item Information Table
Alignment: Assigned AAEC
Depth of Knowledge: Assigned DOK
Mean Score
2
All p-value percentages listed in the item information tables have been rounded.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
4
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
BIOLOGY EXAM DIRECTIONS
Below are the exam directions available to students. These directions may be used to help students
navigate through the exam.
On the following pages of this test booklet are the Keystone Biology Exam questions for Module 1
[or Module2].
There are two types of questions in this module.
Multiple-Choice Questions
These questions will ask you to select an answer from among four choices.
Read each question, and choose the correct answer.
Only one of the answers provided is correct.
Record your answer in the Biology answer booklet.
Constructed-Response Questions
These questions will require you to write your response.
Be sure to read the directions carefully.
You cannot receive the highest score for a constructed-response question without following all
directions.
If the question asks you to do multiple tasks, be sure to complete all tasks.
If the question asks you to explain, be sure to explain. If the question asks you to analyze, describe,
or compare, be sure to analyze, describe, or compare.
All responses must be written in the appropriate location within the response box in the Biology
answer booklet. If you use scratch paper to write your draft, be sure to transfer your final response
to the Biology answer booklet.
In addition, the modules may also include scenarios. A scenario contains text, graphics, charts, and/
or tables describing a biological concept, an experiment, or other scientific research. You can use
the information contained in a scenario to answer certain exam questions. Before responding to any
scenario questions, be sure to study the entire scenario and follow the directions for the scenario.
You may refer back to the scenario at any time when answering the scenario questions.
If you finish early, you may check your work in Module 1 [or Module 2] only.
Do not look ahead at the questions in Module 2 [or back at the questions in Module 1] of your exam
materials.
After you have checked your work, close your exam materials.
You may refer to this page at any time during this portion of the exam.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
5
INFORMATION ABOUT BIOLOGY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SCORING GUIDELINES FOR BIOLOGY
3 Points
The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the scientific content, concepts, and/or
procedures required by the task(s).
The response provides a clear, complete, and correct response as required by the task(s). The
response may contain a minor blemish or omission in work or explanation that does not detract from
demonstrating a thorough understanding.
2 Points
The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the scientific content, concepts, and/or
procedures required by the task(s).
The response is somewhat correct with partial understanding of the required scientific content,
concepts, and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may contain some work
that is incomplete or unclear.
1 Point
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the scientific content, concepts, and/or
procedures required by the task(s).
The response is somewhat correct with minimal understanding of the required scientific content,
concepts, and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may contain some work
that is incomplete or unclear.
0 Points
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the scientific
content, concepts, and/or procedures required by the task(s).
The response may show only information copied or rephrased from the question or insufficient
correct information to receive a score of 1.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
6
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Most prokaryotes and eukaryotes maintain a reserve of ATP. Which feature of prokaryotes and
eukaryotes makes the ATP reserve necessary?
A. They have cell membranes.
B. They can change over time.
C. They use energy to function.
D. They have the ability to reproduce.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.1.1
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 10%
p-value B 8%
p-value C 69% (correct answer)
p-value D 13%
Option Annotations
A. Cell membranes permit the movement of certain materials in and out
of the cell without energy.
B. Change over time is not a process that occurs within an organism’s
lifetime.
C. Key: ATP is the energy currency of a cell, and both prokaryotes and
eukaryotes depend on ATP to fuel their cellular functions.
D. Reproduction primarily involves the distribution of genetic material to
offspring cells.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
7
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
2. Which structure and function are common to all plants and some protists and distinguish
themfrom all animals?
A. chloroplasts that conduct photosynthesis
B. mitochondria that conduct photosynthesis
C. chloroplasts that conduct cellular respiration
D. mitochondria that conduct cellular respiration
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 60% (correct answer)
p-value B 15%
p-value C 15%
p-value D 10%
Option Annotations
A. Key: Chloroplasts, which are absent in all animal cells, convert light
energy into chemical energy within all plants and some protists.
B. Mitochondria perform cellular respiration in all eukaryotic cells, not
photosynthesis.
C. Chloroplasts, which are absent in all animal cells, perform
photosynthesis—not cellular respiration.
D. Mitochondria perform cellular respiration, and they are a shared
characteristic among plants, protists, and animals.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
8
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
3. Which characteristic allows carbon atoms to form chains and rings with other carbon atoms?
A. Carbon has several forms.
B. Carbon can form four covalent bonds.
C. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe.
D. Carbon is a structural part of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 8%
p-value B 63% (correct answer)
p-value C 7%
p-value D 22%
Option Annotations
A. Carbon has several forms, which is a result of its ability to form
chains and rings with other carbon atoms.
B. Key: Carbon forms a variety of chains and shapes because it can
form four covalent bonds with its four valence electrons.
C. Carbon’s abundance makes it available for reactions, but carbon’s
chemical properties permit its bonding variety.
D. Carbon’s presence in the structures of major macromolecules is a
result of its ability to form different types of bonds.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
9
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Use the diagram below to answer question 4.
The title of the diagram is, Cellulose Model. The diagram shows a chain consisting of multiple
three part sequences of a rectangle connected to a hexagon connected to the letter “O”. There
are six rectangles, six hexagons, and five “Os” shown.
4. Cellulose is a carbohydrate and a polymer of glucose. Which statement best describes how
cellulose is formed within living organisms?
A. It is assembled by bonding individual atoms.
B. It is constructed by connecting smaller monomer subunits.
C. It is the product of the decomposition of a much larger molecule.
D. It is the result of a physical change that alters the shape of a compound.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.2.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 25%
p-value B 52% (correct answer)
p-value C 12%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations
A. Glucose is a monomer assembled by bonding individual atoms;
cellulose is a polymer of glucose monomers.
B. Key: Cellulose is a polymer, which is formed when many glucose
monomers bond together.
C. During decomposition, a cellulose polymer breaks down into smaller
monomer subunits.
D. Chemical changes that involve new bond formations between
monomers produce polymers.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
10
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
5. Many plants have a waxy coating on their leaves. Which statement describes the most likely
structure and function of the waxy coating?
A. The waxy coating is a protein that can help attract other organisms for pollination.
B. The waxy coating is a protein that can help release waste molecules during transpiration.
C. The waxy coating is a lipid that can help absorb more sunlight in hot environments.
D. The waxy coating is a lipid that can help prevent excess water loss in dry environments.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.2.3
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 8%
p-value B 9%
p-value C 19%
p-value D 63% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. The waxy coating is a lipid, not a protein.
B. The waxy coating is a lipid, not a protein.
C. The waxy coating helps prevent water loss rather than absorb
sunlight energy.
D. Key: The waxy coating is a type of lipid molecule, and it prevents
water loss due to evapotranspiration.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
11
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
6. The enzyme pepsin is found in the stomach. Which medicine is most likely to directly interfere
with pepsin’s function?
A. a medicine that affects pH
B. a medicine that prevents clotting
C. a medicine that blocks neural impulses
D. a medicine that lowers cholesterol levels
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.3.2
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 52% (correct answer)
p-value B 12%
p-value C 14%
p-value D 21%
Option Annotations
A. Key: Enzymes function within a specific pH range, so a medicine
that alters pH would disrupt the enzyme’s function.
B. A medicine that prevents clotting would interfere with the function of
platelets or proteins in the liquid part of blood.
C. A medicine that blocks neural impulses would disrupt nervous
system function rather than the digestive system.
D. A medicine that lowers cholesterol would likely affect the circulatory
system more than the digestive system.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
12
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
7. Which statement best describes a relationship between mitochondria and chloroplasts?
A. Mitochondria release chemical energy from molecules and store it in chloroplasts.
B. Chloroplasts release chemical energy from molecules and store it in mitochondria.
C. Mitochondria convert chemical energy into light energy that can be used by chloroplasts.
D. Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy that can be used by mitochondria.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 16%
p-value B 20%
p-value C 16%
p-value D 47% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. Mitochondria release chemical energy to fuel cell processes; it is not
stored in chloroplasts.
B. Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of
glucose.
C. Chloroplasts use light energy originally from the Sun, not from
mitochondria.
D. Key: Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy
(glucose), which is used by the mitochondria.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
13
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
8. Which process uses the products of photosynthesis as reactants?
A. active transport
B. cellular respiration
C. DNA replication
D. protein synthesis
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 16%
p-value B 59% (correct answer)
p-value C 9%
p-value D 16%
Option Annotations
A. ATP, a product of cellular respiration, is used to fuel the process of
active transport.
B. Key: Glucose and oxygen are products of photosynthesis that are
also reactants in cellular respiration.
C. DNA replication is a semiconservative process that uses a single
DNA molecule to produce two identical DNA double-helix molecules.
D. The reactants in protein synthesis are amino acids, not the glucose
and oxygen products of photosynthesis.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
14
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
9. Which action is prevented by the plasma membrane?
A. the flow of light into or out of the cell
B. the flow of oxygen into or out of the cell
C. unlimited flow of heat into or out of the cell
D. unlimited flow of water into or out of the cell
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 13%
p-value B 24%
p-value C 16%
p-value D 46% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. The plasma membrane allows the flow of light into or out of a cell.
B. Oxygen is a small molecule and constantly diffuses into the cell for
use in cellular respiration.
C. Heat is a form of energy that moves without restriction in and out of
a cell.
D. Key: Water flow into or out of a cell is limited; it depends on the
solute concentration inside or outside the cell.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
15
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
10. Which transport mechanisms require the formation of a vesicle to transport material into or out
of a cell?
A. diffusion and osmosis
B. exocytosis and endocytosis
C. exocytosis and calcium pumps
D. diffusion and facilitated diffusion
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.1.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 26%
p-value B 51% (correct answer)
p-value C 9%
p-value D 14%
Option Annotations
A. Particle transport during diffusion and osmosis depend on the solute
concentration inside and outside a cell.
B. Key: Exocytosis and endocytosis both require the formation of a
vesicle to carry materials into or out of a cell.
C. Exocytosis requires a vesicle for material transport, but calcium
pumps require energy and protein channels.
D. Particle transport during diffusion depends on the solute
concentration inside and outside a cell, and facilitated diffusion
requires a carrier protein in the plasma membrane.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
16
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
11. The Golgi apparatus is broken down during mitosis and then reformed. Which function would a
cell be unable to perform during the time that its Golgi apparatus is broken down?
A. copying genetic material to include in the new cell
B. forming vesicles to import molecules into the cell
C. processing and packaging proteins for cellular export
D. correcting errors in the process of building a new cell
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.1.3
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 14%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 66% (correct answer)
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations
A. Copying genetic material to include in a new cell occurs in the
nucleus.
B. Vesicle formation to bring materials into the cell occurs at the plasma
membrane.
C. Key: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying and packaging
proteins for secretion from the cell.
D. Both the ribosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum play a role in
checking proteins for errors.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
17
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Directions: Use the information presented on page 17 to answer questions 12 and 13.
Bacteria and Antibiotics
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms. The cell walls of these microorganisms serve as barriers
to chemicals that might affect the processes that occur within a bacterial cell. Antibiotics are a type
of substance used to stop bacterial growth. Some antibiotics cause the bacterial cell wall to rupture.
A diagram is shown. The title of the diagram is, Antibiotic Action on a Bacterium. The left side of the
diagram shows an elliptical shape enclosed with a layered wall, and filled with a substance. There
are two smaller enclosed circular shapes located outside of the larger elliptical shape. The circular
shapes are labeled, antibiotic. The label below the elliptical shape on the left side of the diagram is,
before.
The right side of the diagram shows an elliptical shape enclosed with a layered wall, and filled with
a substance and the two circular shapes inside of the elliptical shape. The wall contains three areas
where the substance has leaked out of the elliptical shape. The leaked out substance is labeled,
rupture. The label below the elliptical shape on the right side of the diagram is, after.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
18
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
12. The function of which human organ is most like the cell walls of bacteria?
A. heart
B. liver
C. pancreas
D. skin
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.1.2.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 6%
p-value B 13%
p-value C 7%
p-value D 74% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. The heart does not provide protection as a regulatory structure.
B. The liver does not provide protection as a regulatory structure.
C. The pancreas does not provide protection as a regulatory structure.
D. Key: The cell walls of bacteria act as regulatory structures similar to
the skin of humans.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
19
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
13. Which statement best describes how antibiotics affect cellular homeostasis?
A. Antibiotics remove chloroplasts from plant cells to cause starvation.
B. Antibiotics interfere with the transport of intracellular and extracellular materials.
C. Antibiotics increase the rate of DNA replication in human cells by forming nucleotides.
D. Antibiotics decrease the rate of cellular respiration in animal cells by producing oxygen.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.4.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 11%
p-value B 62% (correct answer)
p-value C 18%
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations
A. Antibiotics work on bacterial cells, not plant cells. Antibiotics do not
remove chloroplasts.
B. Key: Homeostasis is maintained by different processes to regulate
an organism’s internal environment. The antibiotic action described
in the scenario causes the cell wall to rupture and the cell to burst,
so there can no longer be regulation of transport across the plasma
membrane.
C. Antibiotics do not affect the rate of DNA replication and do not
function against human cells.
D. Antibiotics do not produce oxygen and do not function against
animal cells.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
20
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
14. A student studying muscle contraction made the following hypothesis:
“A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules, but other living body cells will have
less ATP, or none at all.”
The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypothesis was correct, and part was incorrect.
Part A. Describe the role of ATP in the muscle cell.
Part B. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is correct.
Part C. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is incorrect.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
21
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Scoring Guide
#14 Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.3.2.2
Depth of Knowledge 3
Mean Score 1.40
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3 The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical
reactions by describing all three of the following tasks:
describing the role of ATP in the muscle cell AND
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is correct AND
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is incorrect
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2 The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical reactions
by describing any two of the following tasks:
describing the role of ATP in the muscle cell OR
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is correct OR
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is incorrect
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1
The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical reactions
by describing any one of the following tasks:
describing the role of ATP in the muscle cell OR
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is correct OR
giving one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is incorrect
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0
The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the concept
being tested.
Non-
scorables
B – No response written or refusal to respond
F – Foreign language
K – Off task
U – Unreadable
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
22
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Responses that will receive credit:
Part A (1 point):
ATP provides the energy necessary for the muscle to contract.
Part B (1 point):
The student is correct in stating that muscle cells do contain a large number of ATP molecules because
of the energy necessary for repeated contraction.
Part C (1 point):
The student is incorrect in stating that there are living body cells that have no ATP. All living body cells
have ATP. All living body cells need ATP to perform the chemical reactions necessary for life.
Background Information:
ATP is the ubiquitous source of energy currency in living organisms and is found in all living cells. Muscle
cells contain a large number of ATP molecules for the simple reason that a lot of energy is expended in
muscle contraction, but at no time is any living cell entirely devoid of ATP.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
23
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 3 points
14. A student studying muscle contraction made the following hypothesis:
“A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules, but other living body cells will have
less ATP, or none at all.”
The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypothesis was correct, and part was incorrect.
Part A. Describe the role of ATP in the muscle cell.
Student Response: ATP’s purpose is generally to provide energy to a cell so it can carry out
its duties and processes. In a muscle cell, it must igve energy toward
the contraction of that cell and that muscle.
Part B. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is correct.
Student Response: “A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules”. This is
correct. It is because most muscles are used quite often and takes a
large amount of energy to use them. The only way then can get the
higher-than-average amount of energy is to use more ATP molecules.
Part C. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is incorrect.
Student Response: “Other living body cells will have no [ATP] at all”. This is incorrect. Even
though muscle cells need more energy than normal, the other cells still
need energy to function. The way the cells produce their own energy is
making ATP, so if they had no ATP, the cells would die.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical
reactions by describing all three of the tasks presented in the item. The response
describes the role of ATP in the muscle (“ATP’s purpose is generally to provide energy”)
and gives one reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is correct (“muscles are
used quite often and takes a large amount of energy to use them”) and one reason
why part of the student’s hypothesis is incorrect (“other cells still need energy to
function...if they had no ATP, the cells would die”). The response is clear, complete,
and correct.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
24
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 2 points
14. A student studying muscle contraction made the following hypothesis:
“A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules, but other living body cells will have
less ATP, or none at all.”
The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypothesis was correct, and part was incorrect.
Part A. Describe the role of ATP in the muscle cell.
Student Response: ATP is the energy source. So it helps the muscle when it is being
contracted or stretched. The human body uses muscles doing
everything, ATP is the energy helping to move the muscles.
Part B. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is correct.
Student Response: The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypthesis was correct
because a muscle cell does contain a large number of ATP molecules.
Part C. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is incorrect.
Student Response: The student’s techer stated that part of the hypothesis was wrong
because other living body cells can have less ATP but they wont ever
have none at all. A cell cannot function without any ATP at all.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical
reactions by describing two of the tasks presented in the item. The response describes
the role of ATP in the muscle (“ATP is the energy source”) but provides an incomplete
reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is correct. The response correctly states
(“a muscle cell does contain a large number of ATP molecules”) but fails to give the
reason why that part of the hypothesis is correct. The response correctly gives a
reason why part of the student’s hypothesis is incorrect (“cells can have less ATP but
they wont ever have none at all. A cell cannot function without any ATP at all”). The
response contains some work that is incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
25
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 1 point
14. A student studying muscle contraction made the following hypothesis:
“A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules, but other living body cells will have
less ATP, or none at all.”
The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypothesis was correct, and part was incorrect.
Part A. Describe the role of ATP in the muscle cell.
Student Response: The role of ATP in a muscle cell is to give it energy. This is so the
muscle cell can perform actions.
Part B. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is correct.
Student Response: The teacher staid that part of the hypothesis was correct because the
student stated that a muscle cell will have a large amount of ATP.
Part C. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is incorrect.
Student Response: The teacher said that part of the hypothesis was incorrect because the
student stated that other living body cells will have less ATP or none at
all.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the role of ATP in biochemical
reactions by describing one of the tasks presented in the item. The response describes
the role of ATP in the muscle (“The role of ATP in a muscle cell is to give it energy. This
is so the muscle cell can perform actions”) but provides an incomplete reason why
part of the student’s hypothesis is correct. The response correctly states (“a muscle
cell will have a large amount of ATP”) but does not give the reason why that part of the
hypothesis is correct. The response also correctly states the portion of the student’s
hypothesis that is incorrect (“other living body cells will have less ATP or none at all”)
but does not give the reason why that part of the hypothesis is incorrect. The response
contains some work that is incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
26
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 0 points
14. A student studying muscle contraction made the following hypothesis:
“A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules, but other living body cells will have
less ATP, or none at all.”
The student’s teacher stated that part of the hypothesis was correct, and part was incorrect.
Part A. Describe the role of ATP in the muscle cell.
Student Response: ATP in a muscle cell is sappose to help the muscle stay clean.
Part B. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is correct.
Student Response: A muscle cell will contain a large number of ATP molecules because of
the muscle being big.
Part C. Give one reason why the student’s teacher stated that part of the
hypothesis is incorrect.
Student Response: All cells have the same number of ATP in them.
Annotation: The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
role of ATP in biochemical reactions. The response incorrectly describes the role of ATP
in the muscle cell (“to help the muscle stay clean”). Part B provides an incorrect reason
why the student’s hypothesis is correct (“contain a large number . . . because of the
muscle being big”), and Part C incorrectly states the student’s hypothesis is incorrect
because “all cells have the same number of ATP.”

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
27
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
Use the graph and diagram below to answer question 15.
The title of the graph is, Effects of Enzyme A. The label to the left of the graph is, Free Energy.
The vertical line axis is an upward-pointing arrow. The label at the bottom of the graph is,
Reaction Progress. The horizontal line axis is right-pointing arrow.
The graph shows two curves. The top curve is a solid line that starts on the horizontal axis and
forms a bell-shaped curve from left to right. The label on the top curve is, without Enzyme A.
The bottom curve is a dashed line that starts on the horizontal axis and forms a bell-shaped
curve from left to right. The label on the dashed-line curve is, with Enzyme A.
The title of the diagram is, Enzyme A. The left side of the diagram shows an open circle and a
hexagon inside of an irregular shape. The open circle and the hexagon are labeled, active sites.
The right side of the diagram shows an open circle and a hexagon. The open circle and the
hexagon are labeled, substrates.
15.
Part A. Explain how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Be sure to
include energy and time in your answer.
Part B. Conditions around an enzyme change and affect the shape of the
enzyme’s active sites. Predict how this would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
28
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Scoring Guide
#15 Item Information
Alignment BIO.A.2.3.1
Depth of Knowledge 3
Mean Score 0.89
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3 The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the role of an enzyme as a catalyst in
regulating a specific biochemical reaction by
explaining how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction with respect to energy
AND
explaining how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction with respect to time
AND
predicting how changing the shape of the enzyme’s active site would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2 The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the role of an enzyme as a catalyst in
regulating a specific biochemical reaction by fulfilling two of the three bullets listed under the
3-point response.
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1 The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the role of an enzyme as a catalyst in
regulating a specific biochemical reaction by fulfilling one of the three bullets listed under the
3-point response.
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0 The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the concept
being tested.
Non-
scorables
B – No response written or refusal to respond
F – Foreign language
K – Off task
U – Unreadable
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
29
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Responses that will receive credit:
Part A (2 points):
• Enzyme A acts as a catalyst by reducing the activation energy, or the energy that is needed to get
the reaction started. (When the substrates attach to the enzyme’s active sites, they are brought close
together, facilitating the reaction.) The reaction takes less time to occur (“the reaction is faster” is also
acceptable).
Part B (1 point):
• When the shape of an enzyme’s active site is changed, the substrate cannot attach to the active site; it
will not “fit.” The enzyme would not be able to catalyze the reaction.
• When the shape of the enzyme’s active site is slightly changed (caused by a change in pH, for
example), the enzyme activity can become greatly reduced.
(Note: Information in parentheses is not necessary to receive full credit for Part A or Part B.)

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
30
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 3 points
Use the graph and diagram below to answer question 15.
The title of the graph is, Effects of Enzyme A. The label to the left of the graph is, Free Energy.
The vertical line axis is an upward-pointing arrow. The label at the bottom of the graph is,
Reaction Progress. The horizontal line axis is right-pointing arrow.
The graph shows two curves. The top curve is a solid line that starts on the horizontal axis and
forms a bell-shaped curve from left to right. The label on the top curve is, without Enzyme A.
The bottom curve is a dashed line that starts on the horizontal axis and forms a bell-shaped
curve from left to right. The label on the dashed-line curve is, with Enzyme A.
The title of the diagram is, Enzyme A. The left side of the diagram shows an open circle and a
hexagon inside of an irregular shape. The open circle and the hexagon are labeled, active sites.
The right side of the diagram shows an open circle and a hexagon. The open circle and the
hexagon are labeled, substrates.
15.
Part A. Explain how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Be sure to
include energy and time in your answer.
Student Response: Enzyme A acts a catalyst because with enzyme A their is less free
energy being used. With enzyme A, it speeds up the reaction time. That
is how it acts as a catalyst.
Part B. Conditions around an enzyme change and affect the shape of the
enzyme’s active sites. Predict how this would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
Student Response: It would affect the enzyme’s ability to catalyze the reaction because
they might not react right. The active sites could change, and then
they wouldn’t fit like a lock and key anymore, so therefore, the enzyme
would no longer act as a catalyst.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the role of an enzyme as
a catalyst in regulating a specific biochemical reaction by completing all three tasks
presented in the item. The student explains that Enzyme A is a catalyst since the
reaction uses less energy and the reaction time is reduced. The explanation provided
includes both energy and time. In Part B, the student predicts that the enzyme would
not act as a catalyst since the active sites would change. The response is clear,
complete, and correct.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
31
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 2 points
Use the graph and diagram below to answer question 15.
The title of the graph is, Effects of Enzyme A. The label to the left of the graph is, Free Energy.
The vertical line axis is an upward-pointing arrow. The label at the bottom of the graph is,
Reaction Progress. The horizontal line axis is right-pointing arrow.
The graph shows two curves. The top curve is a solid line that starts on the horizontal axis and
forms a bell-shaped curve from left to right. The label on the top curve is, without Enzyme A.
The bottom curve is a dashed line that starts on the horizontal axis and forms a bell-shaped
curve from left to right. The label on the dashed-line curve is, with Enzyme A.
The title of the diagram is, Enzyme A. The left side of the diagram shows an open circle and a
hexagon inside of an irregular shape. The open circle and the hexagon are labeled, active sites.
The right side of the diagram shows an open circle and a hexagon. The open circle and the
hexagon are labeled, substrates.
15.
Part A. Explain how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Be sure to
include energy and time in your answer.
Student Response: Enzyme A acts like a catalyst because it uses less energy and the
reaction time get faster.
Part B. Conditions around an enzyme change and affect the shape of the
enzyme’s active sites. Predict how this would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
Student Response: The enzyme may cause the opposite effects with the catalyze being
used.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the role of an enzyme as a
catalyst in regulating a specific biochemical reaction by completing two of the tasks
presented in the item. The student provides an acceptable response about how
Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction by explaining that less energy is used and
the reaction time is reduced. The prediction of how a change in shape would affect
the enzyme’s ability to catalyze the reaction is unclear. “The enzyme may cause the
opposite effects with the catalyze being used” is not enough for credit. The student
should have more completely described the opposite effects for additional credit. This
response contains work that is incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
32
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 1 point
Use the graph and diagram below to answer question 15.
The title of the graph is, Effects of Enzyme A. The label to the left of the graph is, Free Energy.
The vertical line axis is an upward-pointing arrow. The label at the bottom of the graph is,
Reaction Progress. The horizontal line axis is right-pointing arrow.
The graph shows two curves. The top curve is a solid line that starts on the horizontal axis and
forms a bell-shaped curve from left to right. The label on the top curve is, without Enzyme A.
The bottom curve is a dashed line that starts on the horizontal axis and forms a bell-shaped
curve from left to right. The label on the dashed-line curve is, with Enzyme A.
The title of the diagram is, Enzyme A. The left side of the diagram shows an open circle and a
hexagon inside of an irregular shape. The open circle and the hexagon are labeled, active sites.
The right side of the diagram shows an open circle and a hexagon. The open circle and the
hexagon are labeled, substrates.
15.
Part A. Explain how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Be sure to
include energy and time in your answer.
Student Response: the enzyme A reduces the activation energy
Part B. Conditions around an enzyme change and affect the shape of the
enzyme’s active sites. Predict how this would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
Student Response: Its ability would be to speed up the reaction by reducing the activation
energy
Annotation: The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the role of an enzyme as
a catalyst in regulating a specific biochemical reaction by completing one of the
tasks presented in the item. The student correctly states that Enzyme A reduces the
activation energy but fails to provide any information about the effect on time in the
response. The response in Part B does not correctly answer the question presented
by predicting that the enzyme would catalyze the reaction (which is a repeat of the
information given in Part A). The response contains work that is incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
33
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 0 points
Use the graph and diagram below to answer question 15.
The title of the graph is, Effects of Enzyme A. The label to the left of the graph is, Free Energy.
The vertical line axis is an upward-pointing arrow. The label at the bottom of the graph is,
Reaction Progress. The horizontal line axis is right-pointing arrow.
The graph shows two curves. The top curve is a solid line that starts on the horizontal axis and
forms a bell-shaped curve from left to right. The label on the top curve is, without Enzyme A.
The bottom curve is a dashed line that starts on the horizontal axis and forms a bell-shaped
curve from left to right. The label on the dashed-line curve is, with Enzyme A.
The title of the diagram is, Enzyme A. The left side of the diagram shows an open circle and a
hexagon inside of an irregular shape. The open circle and the hexagon are labeled, active sites.
The right side of the diagram shows an open circle and a hexagon. The open circle and the
hexagon are labeled, substrates.
15.
Part A. Explain how Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. Be sure to
include energy and time in your answer.
Student Response: Enzyme A acts as a catalyst in the reaction because during the reaction
progress the substrates within the active cites of a cell becomes
greater and increases the free energy to a point and then falls slowly.
That is why Enzyme A acts like a catalyst in the reaction.
Part B. Conditions around an enzyme change and affect the shape of the
enzyme’s active sites. Predict how this would affect the enzyme’s ability
to catalyze the reaction.
Student Response: This would affect the enzyme’s ability to catalyze the reaction because
as the conditions around the enzyme change, the enzymes active
sites would change as the substrates of an enzyme change The
oxogen amount, and amount of ATP and Mitochondria also affect the
conditions of an enzyme.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
34
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
Annotation: The response demonstrates an insufficient understanding of the role of an enzyme as a
catalyst in regulating a specific biochemical reaction by not completing any of the tasks
presented in the item. The explanation in PartA does not correctly explain how Enzyme
A acts as a catalyst in the reaction. The student describes the shape of the graph
shown but does not explain the effect Enzyme A would have on the energy or time. The
student does not provide a prediction about how the change in shape would affect the
enzyme’s ability to catalyze the reaction. The response attempts to explain how the
conditions would change and not the effect these changes would have. The response
contains work that is incomplete or unclear.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
35
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
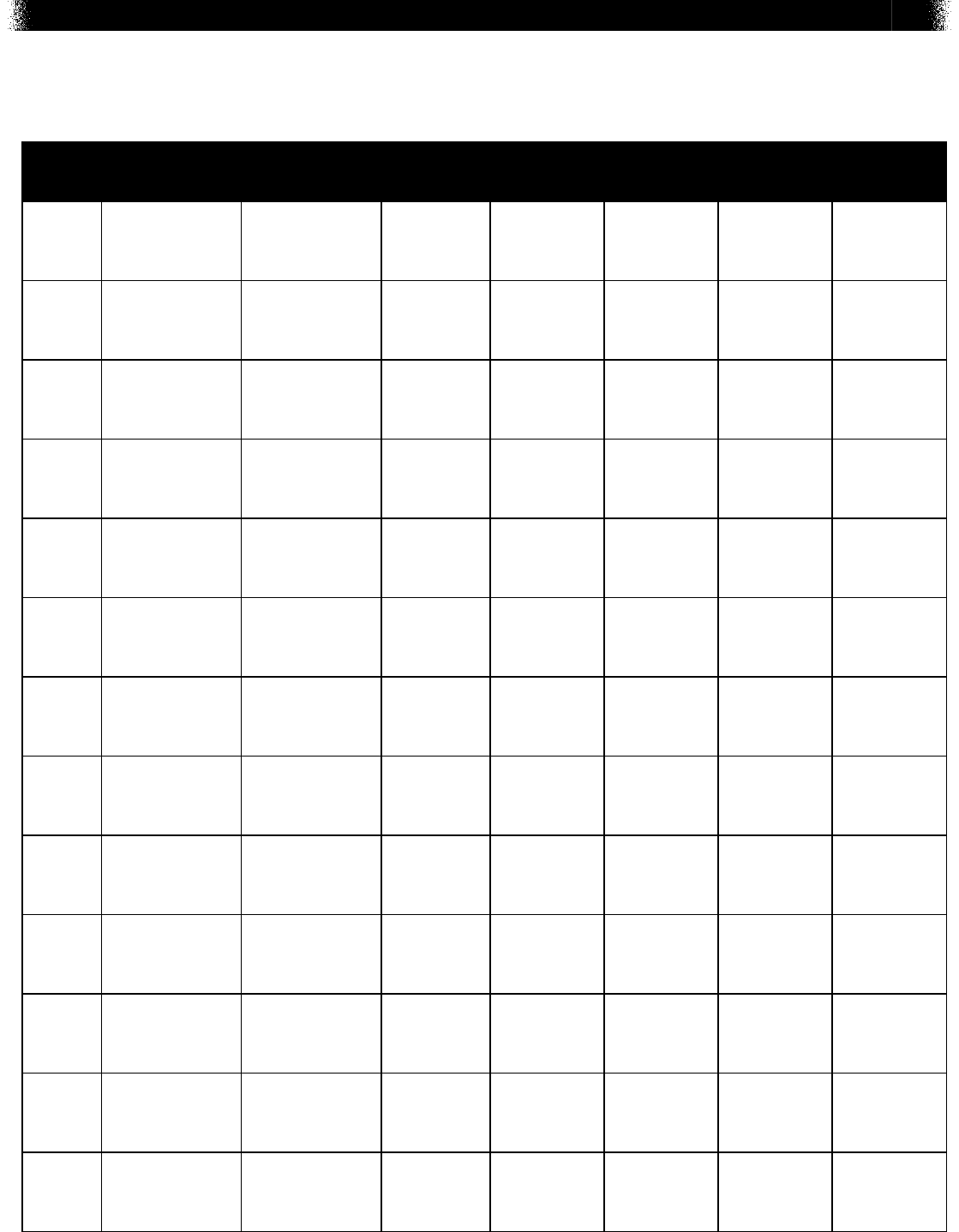
BIOLOGY MODULE 1—SUMMARY DATA
MULTIPLE-CHOICE
Sample
Number
Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 BIO.A.1.1.1 C 2 10% 8% 69%
(correct
answer)
13%
2 BIO.A.1.2.1 A 2 60%
(correct
answer)
15% 15% 10%
3 BIO.A.2.2.1 B 2 8% 63%
(correct
answer)
7% 22%
4 BIO.A.2.2.2 B 2 25% 52%
(correct
answer)
12% 11%
5 BIO.A.2.2.3 D 2 8% 9% 19% 63%
(correct
answer)
6 BIO.A.2.3.2 A 2 52%
(correct
answer)
12% 14% 21%
7 BIO.A.3.1.1 D 2 16% 20% 16% 47%
(correct
answer)
8 BIO.A.3.2.1 B 2 16% 59%
(correct
answer)
9% 16%
9 BIO.A.4.1.1 D 2 13% 24% 16% 46%
(correct
answer)
10 BIO.A.4.1.2 B 2 26% 51%
(correct
answer)
9% 14%
11 BIO.A.4.1.3 C 2 14% 12% 66%
(correct
answer)
8%
12 BIO.A.1.2.2 D 2 6% 13% 7% 74%
(correct
answer)
13 BIO.A.4.2.1 B 2 11% 62%
(correct
answer)
18% 9%
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
36
BIOLOGY MODULE 1
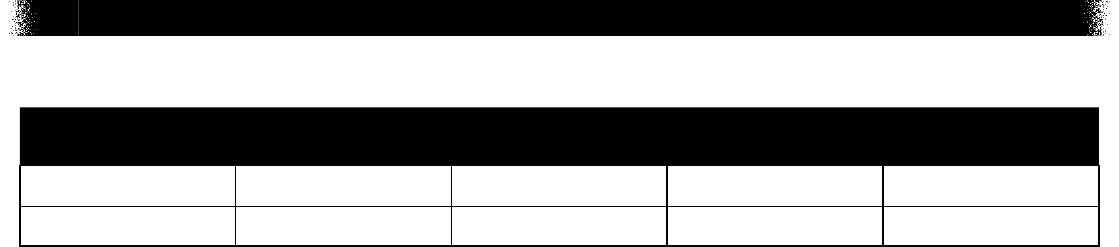
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE
Sample
Number
Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge
Mean Score
14 BIO.A.3.2.2 3 3 1.40
15 BIO.A.2.3.1 3 3 0.89
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
37
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Which statement describes one difference between mitosis and meiosis in animal cells?
A. Mitosis produces sex cells, and meiosis produces diploid cells.
B. Mitosis produces haploid cells, and meiosis produces somatic cells.
C. Mitosis produces four daughter cells, and meiosis produces two diploid cells.
D. Mitosis produces two daughter cells, and meiosis produces four daughter cells.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.1.1.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 19%
p-value B 15%
p-value C 19%
p-value D 46% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. Mitosis produces somatic cells, and meiosis produces haploid cells.
B. Mitosis produces diploid cells, and meiosis produces sex cells.
C. Mitosis produces two diploid daughter cells, and meiosis produces
four haploid daughter cells.
D. Key: Mitosis produces two diploid daughter cells; meiosis produces
four haploid daughter cells.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
38
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
2. Which statement best describes the process by which the millions of body cells that form a
housefly can all contain the same genetic information?
A. Original DNA is duplicated during replication and then distributed into two new cells.
B. Original RNA is duplicated during replication and then distributed into two new cells.
C. Original DNA is duplicated during replication and then distributed into four new cells.
D. Original RNA is duplicated during replication and then distributed into four new cells.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.1.2.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 60% (correct answer)
p-value B 12%
p-value C 23%
p-value D 5%
Option Annotations
A. Key: DNA replication produces two copies of genetic information
that are identical to the original DNA and are distributed into two
new cells.
B. DNA is duplicated during replication, not RNA.
C. DNA replication produces two copies that are distributed to two new
cells, not four.
D. DNA, not RNA, is duplicated during replication and distributed to two
new cells.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
39
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
3. The presence of a specific trait is genetically inherited. There are only two possible outcomes for
this trait: an individual either inherits the trait or does not inherit the trait. Which statement best
describes how parents influence this trait?
A. Each parent contributes two genes for this trait.
B. Each parent contributes one allele for this trait.
C. Each parent contributes two chromosomes for this trait.
D. Each parent contributes one nitrogenous base for this trait.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.1.2.2
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 24%
p-value B 54% (correct answer)
p-value C 17%
p-value D 5%
Option Annotations
A. Each parent contributes one gene for the trait, not two.
B. Key: Each parent contributes one allele for the trait; alleles are
different forms of the same gene.
C. Each parent contributes half of the chromosomes to an offspring
individual, and the chromosomes contain genes that code for
specific traits.
D. Each parent contributes many nitrogenous bases that compose the
large and complex DNA molecule containing thousands of genes
that code for traits.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
40
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Use the diagram below to answer question 4.
DNA Section
A G T G C C G A C arrow original strand
A G G C C G A C arrow altered strand
4. A section of DNA in a cell is altered. Which mutation is being illustrated in the DNA section
above?
A. deletion
B. insertion
C. duplication
D. nondisjunction
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.1.2
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 61% (correct answer)
p-value B 18%
p-value C 11%
p-value D 9%
Option Annotations
A. Key: The altered strand of DNA is shorter than the original strand;
this suggests that one or more bases were deleted.
B. An insertion mutation involves the addition of one or more bases to
the DNA strand, making it longer.
C. A duplication occurs when a section of DNA is copied one or more
times, making the strand longer.
D. Nondisjunction results in one daughter cell having too many
chromosomes or chromatids and the other having none.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
41
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
5. Which statement is true for all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms?
A. Both types of organisms transform energy from sunlight into chemical energy.
B. Both types of organisms assemble proteins through transcription and translation.
C. Both types of organisms are made of cells, tissues, and organs that work together.
D. Both types of organisms have DNA contained within a nucleus as genetic material.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.2.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 14%
p-value B 41% (correct answer)
p-value C 31%
p-value D 14%
Option Annotations
A. Only some prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms can transform
energy from sunlight into chemical energy.
B. Key: Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms assemble proteins
using transcription and translation involving RNA and ribosomes.
C. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms.
D. Prokaryotes have genetic material within circular strands of DNA, but
prokaryotes lack a nucleus.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
42
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Use the diagram below to answer question 6.
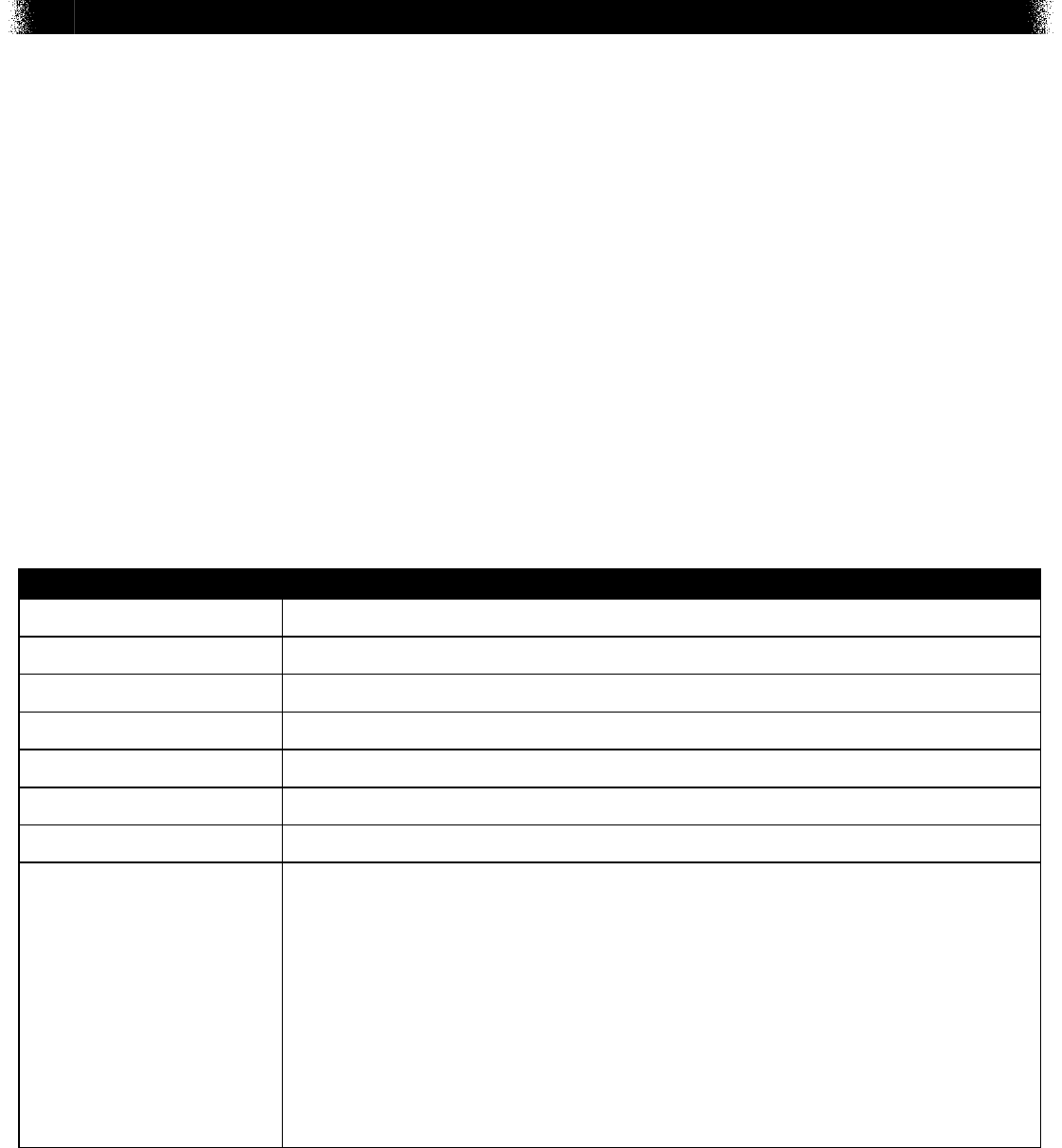
The title of the diagram is, RNA Codon Table. The row header across the top of the table is,
Second Base in Codon. The letters directly under the top row header are, U, C, A, and G. The
column header down the left side of the table is, First Base in Codon. The letters in each box
directly next to the left column header are, U, C, A, and G, respectively. The column header
down the right side of the table is, Third Base in Codon. The letters U, C, A, and G are repeated
in each of the four boxes directly next the right column header.
Each of the sixteen boxes in the middle of the table contain sets of four codes. The codes
starting from the inner top left box from left to right by row, are: Box 1: P-h-e, P-h-e, L-e-u,
L-e-u; Box 2: S-e-r, S-e-r, S-e-r, S-e-r; Box 3: T-y-r, T-y-r, stop, stop; Box 4: C-y-s, C-y-s, stop,
T-r-p; Box 5: L-e-u, L-e-u, L-e-u, L-e-u; Box 6: P-r-o, P-r-o, P-r-o, P-r-o; Box 7: H-i-s, H-i-s,
G-l-n, G-l-n; Box 8: A-r-g, A-r-g, A-r-g, A-r-g; Box 9: I-l-e, I-l-e, I-l-e, M-e-t; Box 10: T-h-r, T-h-r,
T-h-r, T-h-r; Box 11: A-s-n, A-s-n, L-y-s, L-y-s; Box 12: S-e-r, S-e-r, A-r-g, A-r-g; Box 13: V-a-l,
V-a-l, V-a-l, V-a-l; Box 14: A-l-a, A-l-a, A-l-a, A-l-a; Box 15: A-s-p, A-s-p, G-l-u, G-l-u; and Box
16: G-l-y, G-l-y, G-l-y, G-l-y.
6. A mutation occurred that caused a change in an mRNA sequence. The mRNA codon UAC
was replaced by the codon UAA. Which statement describes the most likely outcome of the
mutation?
A. It will produce the same protein using a different set of codons.
B. It will result in an incomplete protein that does not function properly.
C. It will cause mRNA to attach a new amino acid chain during transcription.
D. It will change the bonding pattern between the amino acids joining together.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
43
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.3.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 3
p-value A 12%
p-value B 47% (correct answer)
p-value C 22%
p-value D 19%
Option Annotations
A. Instead of coding for Tyr, this mutation produces a stop, which will
result in the formation of an incomplete protein.
B. Key: The codon UAA codes for a stop, which will result in the
formation of an incomplete protein.
C. The codon UAA codes for a stop, so no additional amino acids will
attach to this protein.
D. Since the mutation codes for a stop, no additional amino acids will
join the protein chain.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
44
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
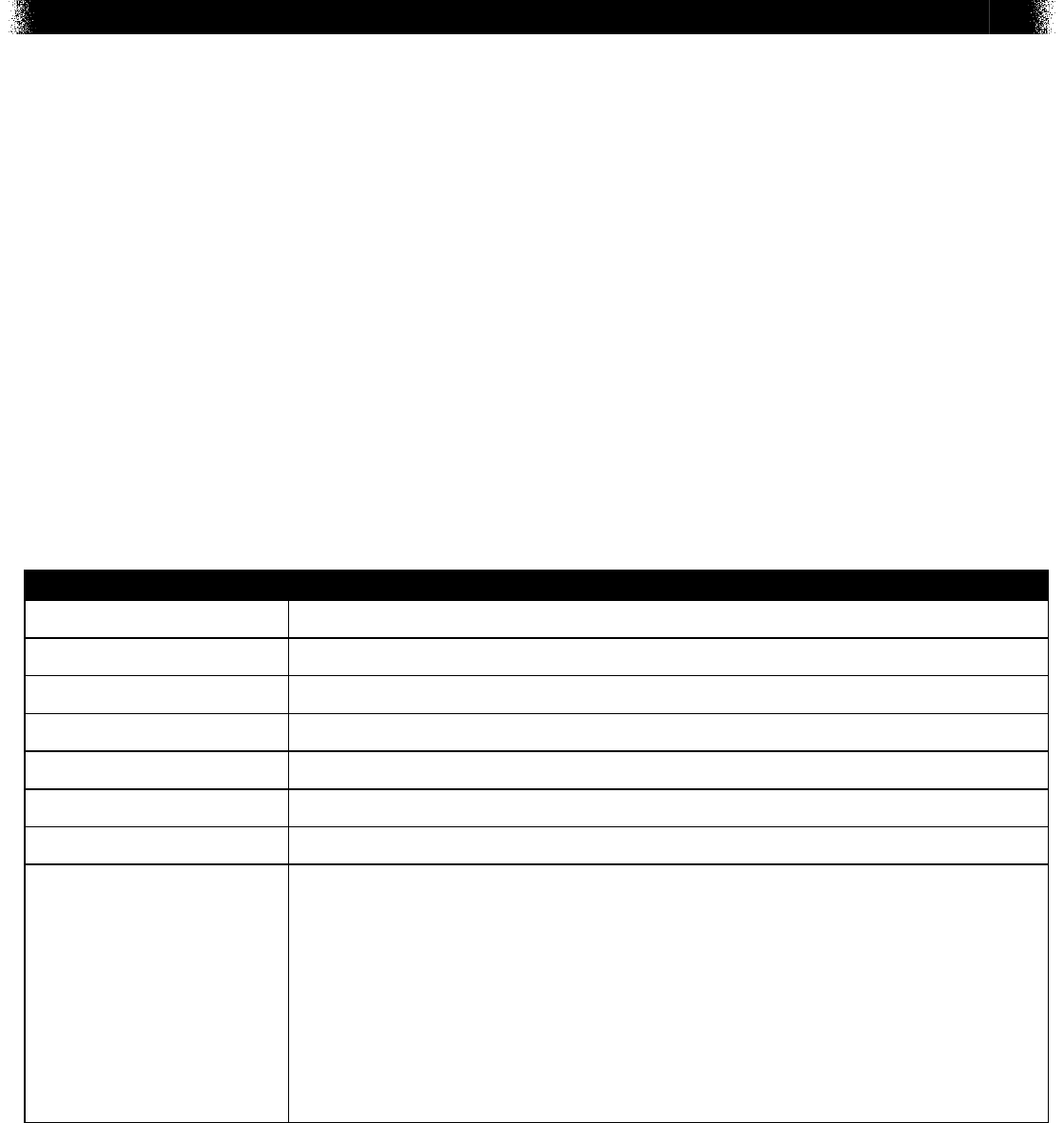
Use the graph below to answer question 7.
The title of the graph is, Color Variation of a Population Twenty Years Ago. The label to the left
of the graph is, Number of Individuals. The label below the graph is, Color Variation. The vertical
axis is an upward pointing arrow. The labels on each end of the horizontal axis from left to right
are, very light brown and very dark brown. The graph shows a curve the goes from near the
top of the vertical axis to near the right end of the horizontal axis. The area below the curve is
shaded from light grey to dark grey from left to right.
7. The graph represents the number of light brown and dark brown organisms living on the
bottomof a clear, sandy lake 20 years ago. Over time, the lake bottom has become covered
with dark sand and sediment. Which change has most likely occurred in the population?
A. The number of light-brown individuals increased.
B. The number of dark-brown individuals increased.
C. The number of light-brown and dark-brown individuals increased.
D. The number of light-brown and dark-brown individuals became equal.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.1.1
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 25%
p-value B 53% (correct answer)
p-value C 11%
p-value D 11%
Option Annotations
A. The number of light-brown individuals decreased because they
blended in less with the dark sand and sediment.
B. Key: The number of dark-brown individuals increased because they
blended in with the dark sand and sediment—enabling them to
survive and reproduce.
C. The number of light-brown individuals decreased, but the number of
dark-brown individuals increased.
D. It is unlikely that the number of light- and dark-brown individuals
became equal because they are unequally adapted to blend into the
environment.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
45
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
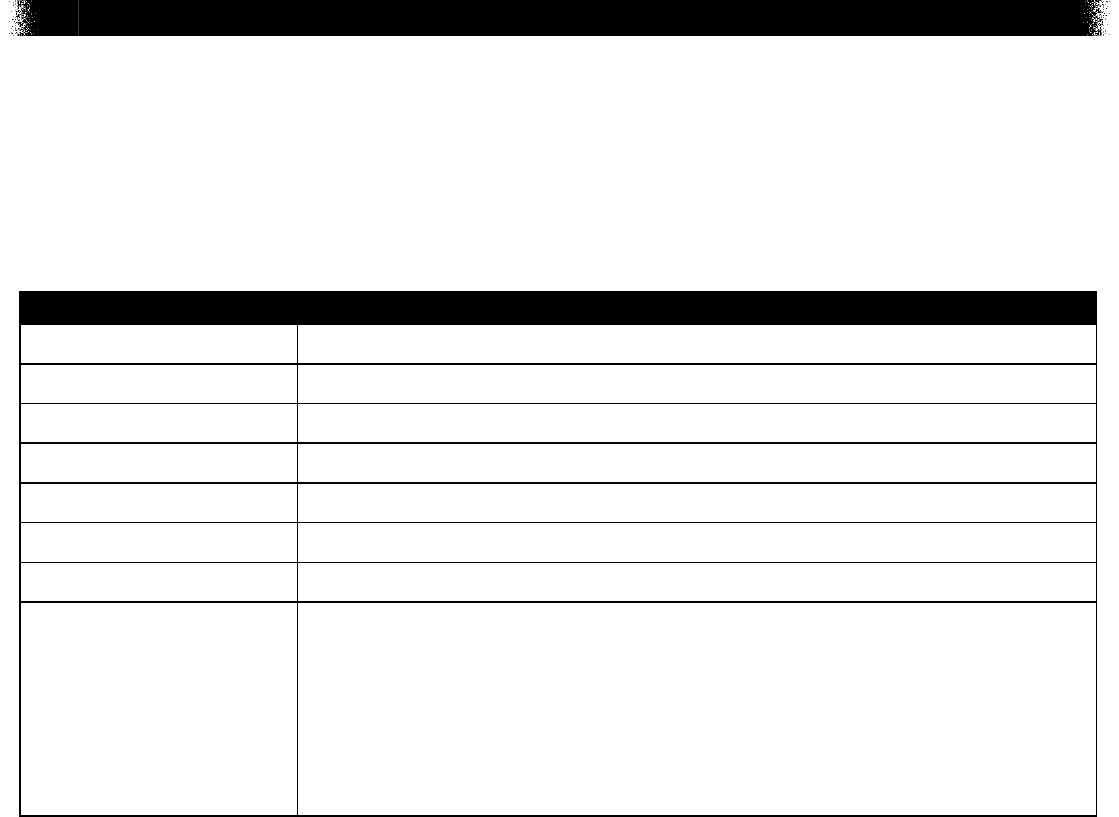
Use the map below to answer question 8.
The title of the map is, The Isthmus of Panama. The map is of Central America. The labels on
the map from the left side in a clockwise direction are, Pacific Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and
Panama. The inset circle to the right of the map shows a magnified view of the Isthmus of
Panama. The label inside of the inset circle is, Panama.
8. The Isthmus of Panama is a narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the
Pacific Ocean. It forms a land bridge that links North and South America. The formation ofthis
isthmus separated two bodies of water that had previously been connected. How did the
formation of this land bridge most likely influence the development of distinct marine species
oneither side of the land bridge?
A. by decreasing genetic drift
B. by causing a founder effect
C. by increasing the rate of genetic mutation
D. by preventing related populations from interacting
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.1.2
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 17%
p-value B 12%
p-value C 15%
p-value D 55% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. Separating populations of marine species may initially reduce their
sizes, thereby increasing genetic drift.
B. A founder effect occurs when a population’s size is rapidly and
drastically reduced; in this case, the populations were separated
gradually and not drastically reduced in size.
C. The rate of genetic mutation is unlikely to be affected by the gradual
separation of a population.
D. Key: Speciation often occurs when populations separate and are no
longer able to interbreed due to physical barriers.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
46
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
9. Which statement describes how a mutation would most likely affect a population?
A. Genotypic variation will increase in the population.
B. Genotypic variation will decrease in the population.
C. The occurrence of a preexisting gene will increase in the population.
D. The occurrence of a preexisting gene will decrease in the population.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.1.3
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 50% (correct answer)
p-value B 17%
p-value C 16%
p-value D 17%
Option Annotations
A. Key: When a mutation occurs within genes, it generates new
genotypic variations within the population.
B. Mutations typically increase, not decrease, genetic variation.
C. There is not enough information provided to predict frequency
changes of preexisting genes.
D. There is not enough information provided to predict frequency
changes of preexisting genes.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
47
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
10. Strep throat is a common human illness often caused by the bacterium Streptococcus
pyogenes. Which term best classifies the colonies of Streptococcus pyogenes in a person with
strep throat?
A. a population
B. an organelle
C. a community
D. an ecosystem
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.1.1
Answer Key A
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 36% (correct answer)
p-value B 27%
p-value C 29%
p-value D 8%
Option Annotations
A. Key: A population is composed of individuals of the same species
(Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria colonies) within a habitat (a
person’s throat).
B. An organelle is a component of a cell.
C. A community is represented by different populations interacting
within the same habitat.
D. An ecosystem includes all the living parts of a habitat along with the
nonliving parts of the habitat that support life.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
48
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
11. Which statement best describes a contribution that decomposers make to an ecosystem?
A. They reduce the atomic mass of carbon atoms.
B. They increase the recycling of carbon-containing molecules.
C. They reduce the total number of carbon atoms in the atmosphere.
D. They increase the total number of carbon nuclei within the atoms.
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.3
Answer Key B
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 13%
p-value B 57% (correct answer)
p-value C 23%
p-value D 6%
Option Annotations
A. Decomposers release carbon into the atmosphere through
respiration, but they do not change carbon’s atomic mass.
B. Key: Decomposers break down remains of once-living organisms,
thereby releasing the carbon from those organisms back into the
atmosphere during respiration.
C. Decomposers add carbon atoms to the atmosphere when they
release carbon during respiration.
D. Each carbon atom has a single nucleus, which is unchanged by
decomposers.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
49
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Directions: Use the information presented on page 49 to answer questions 12 and 13.
The title of the picture is, Aye-aye. The picture shows an aye-aye lemur on a tree branch. The aye-
aye shown has long digits and a long bushy tail.
An aye-aye is a small nocturnal lemur that weighs about four pounds. This endangered species is
found in Madagascar, a large island off the east coast of southern Africa. The main food for aye-ayes
is larvae that live in wood. Aye-ayes find the larvae by tapping on tree branches. They also eat nuts
and fruit. Aye-ayes spend most of their time alone. Each animal occupies about 15 acres and marks
the territory, which alerts other aye-ayes of the boundary.
The title of the map is, Aye-aye Range. A map of Africa is shown. The map shows the outlines of
each country in Africa. The label below the map is, Africa. There is a inset box to the right of the map
showing the island of Madagascar. The map of the island is shaded gray with areas shaded in black.
The label at the top of the inset box is, Madagascar. The Key inside of the inset box shows a black
square labeled Aye-aye range.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
50
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Use the map below to answer question 12.
The title of the map is, Four Locations of Aye-ayes. The map is of the island of Madagascar. The
map is shaded gray with areas shaded in black. The label below the map is, Madagascar. The
labels on the map from the left in a clockwise direction are one, two, three, and four. Each of the
labels is indicating a different area of the diagram that is shaded black.
12. The map indicates four locations of aye-aye populations. Which location would most likely
havean aye-aye population with the greatest variation in allele frequencies?
A. location 1
B. location 2
C. location 3
D. location 4
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.3.1.1
Answer Key D
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 5%
p-value B 8%
p-value C 7%
p-value D 79% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. This location is a small isolated area that would likely have a smaller
population that experiences inbreeding and low genetic diversity.
B. This location is a small isolated area that would likely have a smaller
population that experiences inbreeding and low genetic diversity.
C. This location is an isolated area that would likely have a smaller
population and less genetic diversity than the largest location.
D. Key: This population occupies the largest area of the island, which
likely has a more diverse environment than the other locations; its
population is likely much larger than the other populations, resulting
in a greater variation in allele frequencies.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
51
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
13. For the aye-aye species, what is most likely the primary value of individuals living alone?
A. decreased space needs for the species
B. increased survival rates with habitat loss
C. reduced competition for natural resources
D. greater genetic variability within the species
Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.2
Answer Key C
Depth of Knowledge 2
p-value A 11%
p-value B 17%
p-value C 64%
p-value D 8% (correct answer)
Option Annotations
A. A population with individuals living alone likely requires more rather
than less habitat space.
B. An increase in habitat loss would not increase survival rates among
individuals that require large solitary territories.
C. Key: Individuals who live alone in a territory have the resources they
need within their territory and are less likely to compete for resources
such as shelter, food, and water.
D. Living alone, rather than in groups, often results in increased
difficulty in finding mates, which could result in fewer chances of
increasing genetic variability within a population or species.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
52
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
14. State officials are considering constructing a road through a forested wilderness area. This
action will likely affect the forest ecosystem in various ways.
Part A. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in
the forest ecosystem.
Part B. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals
in the forest ecosystem.
Part C. Describe one way that the construction of a road could have a positive
effect on the forest ecosystem.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
53
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Scoring Guide
#14 Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.4.2.4
Depth of Knowledge 3
Mean Score 1.89
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3 The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how ecosystems change in
response to natural and human disturbances (e.g., climate changes, introduction of nonnative
species, pollution, fires) by
predicting how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in the forest
ecosystem and
predicting how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals in the forest
ecosystem and
describing one way that the construction of a road could have a positive effect on the forest
ecosystem.
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2 The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how ecosystems change in response
to natural and human disturbances (e.g., climate changes, introduction of nonnative species,
pollution, fires) by fulfilling two of the three bullets listed in the 3-point response.
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1 The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how ecosystems change in response
to natural and human disturbances (e.g., climate changes, introduction of nonnative species,
pollution, fires) by fulfilling one of the three bullets listed in the 3-point response.
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0 The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the concept
being tested.
Non-
scorables
B – No response written or refusal to respond
F – Foreign language
K – Off task
U – Unreadable
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
54
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Responses that will receive credit:
Part A (1 point):
• Many trees and other plants will be destroyed during the construction.
• Removal of trees causes an increase in sunlight reaching the forest floor. Plants that cannot tolerate
the increased sunlight will not survive.
• Removal of trees and construction of dark-colored roads could increase the surface temperatures of
the forest area, which some plants may not be able to tolerate.
• Dust from road traffic may settle on plants and disrupt photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration.
• Emissions from vehicles and chemicals used for de-icing roads can contaminate the air and soil,
causing damage or death to plants.
• A road could affect natural water drainage patterns in the area, which could harm some plants.
• Vehicles on the road could spill chemicals or waste that could harm plants.
Part B (1 point):
• Some animals could be struck by vehicles. Some animals are attracted to roads for warmth, dust, salt,
gravel, or roadside vegetation. These animals are vulnerable to traffic. Some animals may be killed
during the construction.
• Animals’ habitats will be divided into sections. Animals may become separated from some food
sources. (Some animals are averse to crossing roads, and will not cross even very narrow roads.)
• Animals’ habitats will be fragmented. This will effectively reduce the population of some species.
These species will be vulnerable to problems that arise from having a small gene pool, such as genetic
deterioration from inbreeding.
• Animals that depend on plants that have been destroyed will not survive, unless they find another food
source.
• Vehicles on the road could spill chemicals or waste that could harm animals.
Part C (1 point):
• An increase in roads could bring more visitors to an area, which could increase awareness about the
area and cause some people to take on the cause of restoring or protecting wilderness areas.
• An increase in roads could cause easier access to wilderness areas, allowing more people to
experience and appreciate nature, leading to increased funding for the forest ecosystem.
• By the state allowing a road through a particular forested area, another area may be protected from
human disturbances.
• The road may allow new species to populate the area. These species could be more capable of
survival in the new environment.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
55
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 3 points
14. State officials are considering constructing a road through a forested wilderness area. This
action will likely affect the forest ecosystem in various ways.
Part A. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in
the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Many plants that are already living in the forest will be destroyed and
gotten rid of in order to make room for the new road. The forest will
have less organisms, and if one species existed in a concentrated area
that happened to be where the road was constructed, the forest will
also have less species because some might be killed out entirely from
that area.
Part B. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals
in the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Many animals will lose their homes by the construction of a road.
Animals that live in underground burrows might lose their homes
because the road will be built right overtop of them. Animals that live
in plants and trees might lose their homes because they will have to
be cut down in order to make room for the road. Also, animals might
experience food shortages, as there will be much less plants for them
to eat. These plants would be removed for the construction of the road,
and certain animals might depend on those plants for survival, whether
it be for food or shelter.
Part C. Describe one way that the construction of a road could have a positive
effect on the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Building a road through the forest might have the positive effect of
letting more light in. Because several trees will be cleared away, there
will be more open space and more areas where the sun and sky are
not blocked out. Therefore, more plants might be given access to this
new light and will grow more rapidly as well as more healthily, and even
taller. Also, different species of plants that require excessive amounts
of sunlight will be able to grow in these areas that were not previously
able to grow there due to the canopy of trees.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
56
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Annotation: The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how ecosystems change
in response to natural and human disturbances by fulfilling all three of the tasks
presented in the item. The response correctly predicts how the construction of a road
could negatively affect plants in the forest ecosystem (“Many plants that are already
living in the forest will be destroyed . . . the forest will also have less species”) and
predicts how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals in the forest
ecosystem (“animals will lose their homes . . . might experience food shortages”). The
response also correctly describes one way that the construction of a road could have
a positive effect on the forest ecosystem (“trees will be cleared away . . . the sun and
sky are not blocked out . . . plants might be given access to this new light and will grow
more rapidly”). The response is clear, complete, and correct.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
57
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 2 points
14. State officials are considering constructing a road through a forested wilderness area. This
action will likely affect the forest ecosystem in various ways.
Part A. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in
the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Building a road through the forest ecosystem could allow fumes from
car exhausts to travel and kill plants in the area.
Part B. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals
in the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: The construction of a road in the forest ecosystem would kill the plants
which would give animals less to eat thus creating a decrease in
population.
Part C. Describe one way that the construction of a road could have a positive
effect on the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: The construction of the road would allow animals to interact with
humans.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how ecosystems change in
response to natural and human disturbances by fulfilling two of the tasks presented
in the item. The response correctly predicts how the construction of a road could
negatively affect plants in the forest ecosystem (“car exhausts . . . kill plants in the
area”) and predicts how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals in
the forest ecosystem (“construction . . . would kill the plants which would give animals
less to eat”). The response fails to completely describe one way the construction of
a road could positively affect the ecosystem. “Allow animals to interact with humans”
does not clearly describe a positive effect. The response contains some work that is
incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
58
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 1 point
14. State officials are considering constructing a road through a forested wilderness area. This
action will likely affect the forest ecosystem in various ways.
Part A. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in
the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: It could affect it by the run of the engines, because the engines would
give off carbon monoxide, which is not very good for the environment.
Part B. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals
in the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Like I said before carbon manoxide would kill of the animals because
they wouldnt be able to breathe that fresh air. instead they would be
breathing bad air which could kill the organisms off face of the earth.
Also if they would have to knock down trees, then the animals would
have no place to stay.
Part C. Describe one way that the construction of a road could have a positive
effect on the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: Because it would give the ecosystem a source of energy.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how ecosystems change in
response to natural and human disturbances by fulfilling one of the tasks presented
in the item. The response (“the engines would give off carbon monoxide . . . not very
good for the envrionment”) does not clearly predict how construction could negatively
affect plants in the forest ecosystem and earns no credit, but the response does
correctly predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals in the
forest ecosystem (“carbon manoxide would kill of the animals . . . knock down trees,
then the animals would have no place to stay”) and earns credit. The description (“it
would give the ecosystem a source of energy”) is not complete enough to describe a
positive effect on the forest ecosystem for credit. The response contains work that is
incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
59
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Online Response Score: 0 points
14. State officials are considering constructing a road through a forested wilderness area. This
action will likely affect the forest ecosystem in various ways.
Part A. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect plants in
the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: By the heat and the motion of the construction trucks.
Part B. Predict how the construction of a road could negatively affect animals
in the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: By the human seeing, and by the sounds of the construction workers.
Part C. Describe one way that the construction of a road could have a positive
effect on the forest ecosystem.
Student Response: By the equipment and the road matterial used.
Annotation: The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of how
ecosystems change in response to natural and human disturbances. The response
(“by the heat and the motion of the construction trucks”) does not clearly predict
how construction could negatively affect plants in the forest ecosystem and earns no
credit; also the response does not clearly predict how construction of a road could
negatively affect animals in the forest ecosystem (“human seeing, and by the sounds of
the construction workers”). The description (“by the equipment and the road matterial
used”) is not complete enough to describe a positive effect on the forest ecosystem for
credit.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
60
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE ITEM
15. New technologies can extract certain oils from plants to make renewable biodiesel fuel.
Scientists have altered the genome of a species of plant to increase the amount of this oil that
each plant produces. To do this, scientists activated a gene that directs cells to store plant oils.
To further increase the amount of plant oil produced, scientists are planning to duplicate the
gene that codes for oil production.
Part A. Describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is
similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations.
Part B. Explain how this process could impact agriculture in the United States.
Part C. Explain how altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of
medicine.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
61
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Scoring Guide
#15 Item Information
Alignment BIO.B.2.4.1
Depth of Knowledge 3
Mean Score 1.26
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline
Score Description
3 The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how genetic engineering has
impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing all three of the
following tasks:
describing how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar to naturally
occurring genetic mutations AND
explaining how this process could impact agriculture in the United States AND
explaining how altering the genome of a species could impact the field of medicine
The response is clear, complete, and correct.
2 The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how genetic engineering has impacted
the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing two of the following tasks:
describing how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar to naturally
occurring genetic mutations OR
explaining how this process could impact agriculture in the United States OR
explaining how altering the genome of a species could impact the field of medicine
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
1 The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how genetic engineering has
impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing one of the following
tasks:
describing how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar to naturally
occurring genetic mutations OR
explaining how this process could impact agriculture in the United States OR
explaining how altering the genome of a species could impact the field of medicine
The response may contain some work that is incomplete or unclear.
0 The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of the
concept being tested.
Non-
scorables
B – No response written or refusal to respond
F – Foreign language
K – Off task
U – Unreadable
Note: No deductions should be taken for misspelled words or grammatical errors.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
62
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Responses that will receive credit:
Part A (1 point):
• The naturally occurring mutation could cause a similar effect as the scientific duplicating of a gene.
• The scientists’ plan to alter the plant’s gene uses a naturally occurring type of mutation.
Part B (1 point):
• This process could impact agriculture by reducing the demand for fossil fuels. Currently, fossil fuels
are used extensively in agriculture, but if plants produce oil on a large scale, then the agricultural
industry becomes more sustainable in terms of its fuel use.
• This process could impact agriculture in the United States by improving agricultural profits by giving
farmers an additional way to earn revenue: from the plant oils, and from the food products being
grown.
• This process could impact agriculture by increasing the amount of land devoted to agriculture in order
to produce more of this plant-based oil.
• Or any other scientifically sound impact to agriculture
Part C (1 point):
• It allows for more treatment options for genetic disorders using techniques like gene therapy.
• Altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of medicine by giving scientists and
researchers the additional experience and expertise in genetics that might allow for continued medical
therapies for genetic disorders in humans or animals.
• Being able to modify the genetic code of an embryo to prevent the development of genetically
inherited conditions.
• Or any other scientifically sound impact on the field of medicine

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
63
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 3 points
15. New technologies can extract certain oils from plants to make renewable biodiesel fuel.
Scientists have altered the genome of a species of plant to increase the amount of this oil that
each plant produces. To do this, scientists activated a gene that directs cells to store plant oils.
To further increase the amount of plant oil produced, scientists are planning to duplicate the
gene that codes for oil production.
Part A. Describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is
similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations.
Student Response: Naturally occuring genetic mutations will alter the plant’s performance
exactly like artificially modifying its genome, but it is entirely random
and could take a very long time to get the right trait. Artificial
modification is quick and not too difficult.
Part B. Explain how this process could impact agriculture in the United States.
Student Response: The mass planting of biodiesel fuel plants could cause the agriculture
industry to explode and farmers could make money, but other plants
may suffer when they begin recieving less attention. That is, tomatos
could be improperly taken care of and all of a sudden the population
and quality of the vegetable will drop.
Part C. Explain how altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of
medicine.
Student Response: Genome altering has allowed us to produce more life-saving plants
used in medicines and in the future may be able to make things
immune to certain diseases.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of how genetic engineering
has impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing all three
tasks. The response correctly describes how the altering of the plant’s genome by
the scientists is similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations (“Naturally occuring
genetic mutations will alter the plant’s performance exactly like artificially modifying
its genome”) and correctly explains how this process could impact agriculture in the
United States (“cause the agriculture industry to explode and farmers could make
money”). The response also correctly explains how altering the genome of a species
could impact the field of medicine (“genome altering has allowed us to produce more
life-saving plants used in medicines”). The response is clear, complete, and correct.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
64
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 2 points
15. New technologies can extract certain oils from plants to make renewable biodiesel fuel.
Scientists have altered the genome of a species of plant to increase the amount of this oil that
each plant produces. To do this, scientists activated a gene that directs cells to store plant oils.
To further increase the amount of plant oil produced, scientists are planning to duplicate the
gene that codes for oil production.
Part A. Describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is
similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations.
Student Response: The plant could have experienced this alteration in its natural
environment from some sort of drastic change.
Part B. Explain how this process could impact agriculture in the United States.
Student Response: This could produce more farming jobs and let us not have to buy our oil
from Iraq.
Part C. Explain how altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of
medicine.
Student Response: If there is a plant that produces a specific chemical that is beneficial to
the medical field, it’s genes could be altered to make it produce more of
that specific chemical.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a partial understanding of how genetic engineering has
impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing two of the
tasks. The response (“the plant could have experienced this alteration in its natural
environment from some sort of drastic change”) does not completely describe how the
altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar to naturally occurring genetic
mutations. The response correctly explains how the process could impact agriculture in
the United States (“produce more farming jobs”) and correctly explains how altering the
genome of a species could impact the field of medicine (“plant that produces a specific
chemical . . . altered to make it produce more of that specific chemical”). The response
contains some work that is incomplete or unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
65
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 1 point
15. New technologies can extract certain oils from plants to make renewable biodiesel fuel.
Scientists have altered the genome of a species of plant to increase the amount of this oil that
each plant produces. To do this, scientists activated a gene that directs cells to store plant oils.
To further increase the amount of plant oil produced, scientists are planning to duplicate the
gene that codes for oil production.
Part A. Describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is
similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations.
Student Response: if you alter a plant’s genome your not directly altering their
chromosomes it does it naturally and a genetic mutation alter’s the
chromosome naturally.
Part B. Explain how this process could impact agriculture in the United States.
Student Response: More plants would be going for the creation of biodiesel fuel to make
more money from that.
Part C. Explain how altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of
medicine.
Student Response: Altering the genome of a species can change it’s life they could be born
with brown eyes instead of the genetic codon of blue or Hazel and a
downs baby could be born normal.
Annotation: The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of how genetic engineering has
impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture by completing one of the
tasks. The description of altering the plant’s chromosomes in PartA does not correctly
describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar to naturally
occurring genetic mutations. The response (“more plants . . . make more money from
that”) in Part B correctly explains how the process could impact agriculture in the
United States, but the response in Part C (“could be born with brown eyes instead
of...blue or Hazel”) does not correctly explain how altering the genome of a species
could impact the field of medicine. The response contains work that is incomplete or
unclear.

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
66
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
STUDENT RESPONSE
Handwritten Response Score: 0 points
15. New technologies can extract certain oils from plants to make renewable biodiesel fuel.
Scientists have altered the genome of a species of plant to increase the amount of this oil that
each plant produces. To do this, scientists activated a gene that directs cells to store plant oils.
To further increase the amount of plant oil produced, scientists are planning to duplicate the
gene that codes for oil production.
Part A. Describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is
similar to naturally occurring genetic mutations.
Student Response: It is similar because they both require a gene that will duplicate to form
biodiesel fuel.
Part B. Explain how this process could impact agriculture in the United States.
Student Response: it could impact farmers because their crops could die due to too much
air pollution for the Biodiesel fuel.
Part C. Explain how altering the genome of a species has impacted the field of
medicine.
Student Response: because of how medicine is being used in our daily life. Doctors are
writing more and more prescriptions.
Annotation: The response provides insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of how
genetic engineering has impacted the fields of medicine, forensics, and agriculture. The
response (“they both require a gene that will duplicate to form biodiesel fuel”) does not
correctly describe how the altering of the plant’s genome by the scientists is similar
to naturally occurring genetic mutations. The response (“crops could die due to too
much air pollution”) in Part B does not clearly explain how the process could impact
agriculture in the United States, and the response in Part C (“doctors are writing more
and more prescriptions”) does not completely explain how altering the genome of a
species could impact the field of medicine.
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
67
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
BIOLOGY MODULE 2—SUMMARY DATA
MULTIPLE-CHOICE
Sample
Number
Alignment Answer Key
Depth of
Knowledge
p-value
A
p-value
B
p-value
C
p-value
D
1 BIO.B.1.1.2 D 2 19% 15% 19% 46%
(correct
answer)
2 BIO.B.1.2.1 A 2 60%
(correct
answer)
12% 23% 5%
3 BIO.B.1.2.2 B 2 24% 54%
(correct
answer)
17% 5%
4 BIO.B.2.1.2 A 2 61%
(correct
answer)
18% 11% 9%
5 BIO.B.2.2.1 B 2 14% 41%
(correct
answer)
31% 14%
6 BIO.B.2.3.1 B 3 12% 47%
(correct
answer)
22% 19%
7 BIO.B.3.1.1 B 2 25% 53%
(correct
answer)
11% 11%
8 BIO.B.3.1.2 D 2 17% 12% 15% 55%
(correct
answer)
9 BIO.B.3.1.3 A 2 50%
(correct
answer)
17% 16% 17%
10 BIO.B.4.1.1 A 2 36%
(correct
answer)
27% 29% 8%
11 BIO.B.4.2.3 B 2 13% 57%
(correct
answer)
23% 6%
12 BIO.B.3.1.1 D 2 5% 8% 7% 79%
(correct
answer)
13 BIO.B.4.2.2 C 2 11% 17% 64%
(correct
answer)
8%
Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
68
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
CONSTRUCTED-RESPONSE
Sample
Number
Alignment Points
Depth of
Knowledge
Mean Score
14 BIO.B.4.2.4 3 3 1.89
15 BIO.B.2.4.1 3 3 1.26

Pennsylvania Keystone Biology Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2016
69
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
BIOLOGY MODULE 2
Keystone Exams
Biology
Item and Scoring Sampler
2016–2017
Copyright 2016 by the Pennsylvania Department of Education. The materials contained in this
publication may be duplicated by Pennsylvania educators for local classroom use. This permission
does not extend to the duplication of materials for commercial use.
